Google has over 200 ranking factors in its algorithm that decides on which pages to rank for particular terms in the search engine results pages. Such a daunting number, isn’t it? The prospect of setting up your pages for all those 200 ranking factors to make your pages favorable to Google can look like such a difficult task to do. This is where we come in, we give you a list of the top ranking factors to start doing, to help you get started in optimizing your pages to get to the top of search engine rankings.
Plus, we give you the #1 seo ranking factor for 2021 that have withstood the test of time and that all your pages must have. Start with these ones and you are on your way to getting your page ranked up in search engines. We provide you the roadmap, no need to get confused going for all 200, we give you the must dos.
But first, let’s start by having a clear idea of what we’re talking about.
You probably know that search engines are run by algorithms that determine which results are shown first, second…and last.
And you’re likely here because you’re wondering why search engines choose to display a web page (yours, hopefully) first on a search engine results page (SERP) for a given query/keyword.
Now, I have some bad news for you: no one knows Google’s exact ranking algorithm.
But we do feel that there are variables (or ranking factors, ranking signals) that guide these algorithms.
The SEO Intelligence Agency has done tests and experiments to determine which of these factors are being considered by search engines in ranking a page.
Below, we’ll go through a number of Google’s ranking factors that may be known and not-so-well-known.
That said, we feel that there’s one that guides them all.
As you read these words, this #1 ranking factor is at work–right now.
The fact that you’re following what I’m saying is proof of this #1 ranking factor.
So, what is the #1 most important ranking factor?
“Me?” You ask.
Yes, and more specifically, I mean that your experience, how well the web page fulfills your search query and search intent (what you typed in the search engine) is the most important factor that determines if and where a page is ranked.
And when you consider that Google wants to return the best search results to real, human visitors, it’s easy to understand that the user experience (sometimes known as UX), is ultimately the #1 guiding factor.
I know this seems obvious, and it is, but it’s worth mentioning because although we’ll list some other ranking factors below, those factors should be used in conjunction with the user’s experience.
Too often, we (as online businesses) get lost in the detail and minutia of implementing these factors. Unfortunately, some can lose sight of the end goal of their efforts.
So, now that we’ve established that, what are the other factors that search engines use to rank web pages?

Now that you know that Google’s aim is to return the best search result to its searchers, we can reason that Google wants all search engine optimization efforts to be pointed toward that goal.
Pleasing your audience is pleasing Google.
That said, optimizing for search helps the algorithm determine what your page is about, and create relevancy between your page and the particular target keyword being used in a search query.
Once the relevancy has been established and you have the search visibility, it is up to the user to judge if your page satisfies their reason for doing the Google search. User satisfaction and user engagement are part of what Google considers when ranking a page.
The search algorithm may deem your page relevant and but when it sees that the user is not satisfied with your page during their search experience, then, you will not get ranked.
Ranking factors can be categorized into 3 types:
Technical ranking factors are factors that are…well…technical and it deals with the performance of your website. The response time of your server (which helps determine your page speeds) and how secure your site is are both examples of technical ranking factors. Your site’s core web vitals are also part of technical SEO (you can check your site’s metrics in Google Search Console) There can be a bit of overlap between technical and on-page factors.
On-page–and maybe on-site–ranking factors are ones that are thought to be mostly in the control of the webmaster, or business. They range from the keywords you target to the readability of your content.
In short, on-page ranking factors are variables having to do with your site that Google (and other search engines) use to determine where your site ranks for a given search query.
Off-page ranking factors are, as the word implies, ranking factors that aren’t on your site, and to some extent, may not be in your control.
For example, when another site decides to link to yours, that’s an off-page ranking factor, because it’s not something you control.
That said, there are link-building efforts where some sites can control the incoming links from other sites, but even then, those links are still seen as off-page ranking factors.)

Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness is what EAT stands for, and this acronym came to light after an August 2018 Google updated that people call the “medic” update.
E-A-T matters because for the YMYL (Your Money, Your Life) subjects, where people can be searching for information on important life issues (finances, health, etc.), Google wants to be sure it returns results from authors with EAT. Google would prefer to show you a site staffed with credited experts, rather than a blog post made by some unknown person.
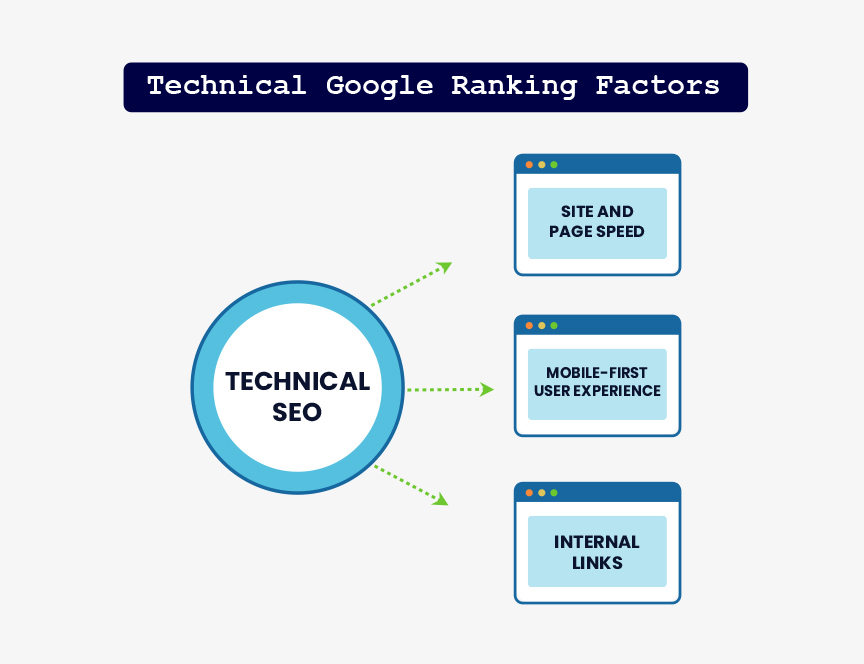
In a way, technical ranking factors are the most important, because if you don’t have a site, then nothing else in SEO really matters.
There are some who say the older the domain, the better the rank. Also, that the longer the registration of your domain, the better because it shows that the owner has a longer-term aim.
Domain history is important (particularly if you like to buy expired domains) because a domain’s reputation and domain authority tends to follow it. For example, if it had health content before, it should have health content in its current iteration.
For location- or country-specific sites, the TLD (top-level domain) extension (.us, .jp, .co.uk, .ca, .fr, etc.) is a good indication that the site is for users of a given country or geographic area.
Though this may not be a direct ranking factor, it is an indirect one, because bounce rate (how many people leave a page) is important.
It’s been said that the longer people have to wait for a page to load, the more likely they are to exit that page.
That’s why it’s important that your pages load quickly–in 3 seconds or less.
We have tests and articles on page speed and bounce rate that you may be interested to read about. There are tips on improving your page speed and bounce rate that can help you with improving these factors on your page.
More and more, Google is preferring the mobile version of a site rather than the desktop version, especially since more and more mobile users are using their mobile devices rather than desktop. Due to this, more people are doing mobile search. If your site is responsive (meaning that it’ll display in conjunction with the screen dimensions of the user’s device), then this is mostly taken care of.
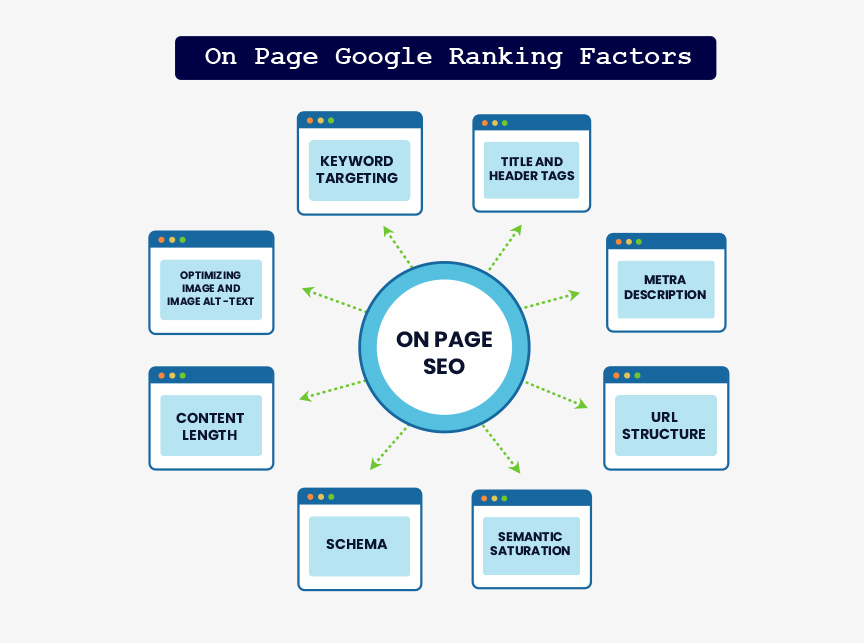
As I mentioned earlier, on-page ranking factors are easier to control than off-page ranking factors. On-page factors include the following:
Searchers use search queries (that is, what they type into a search box) to search, so it makes perfect sense that Google would want to display results that pertain to that search query. If Google thinks that the content of your page pertains to that search query (matches that keyword phrase), then Google may use that to determine where your page ranks.
A way to do this is to use the target keyword in your content and on some of the critical on page factors that robots look to when it tries to determine what a page is about. That said, avoid keyword stuffing or using your target keywords repeatedly that it becomes too much as this could cause you more harm than good. Take note of the right keyword density for your page by doing competitive analysis of your competitors that are ranking for your search term.
This has to do with the code of your web page, which is usually unseen (though some website platforms place visual emphasis on header tags).
Just as the text in the title of a book or article helps us determine if we’ll read it, the text that makes up the title of a document (web page) has great importance.
If the text in a title gives the document its name, then the header tags serve as sections within that document.
The text in these key areas is important on-page ranking factors because it tells the search engine what the document (web page) is about.
The title is also the one displayed in the search query and having your keyword in the title, aside from letting search engines know what your page is about, helps users also determine the topic of your page, if what they are searching for is on your page, and if they should click on your page.
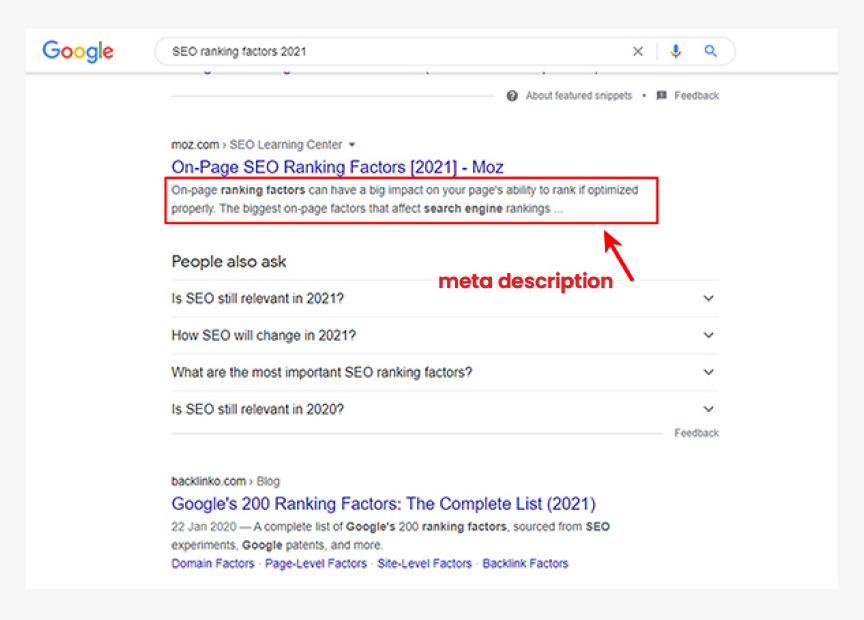
A meta description is an unseen portion of the web page. It’s basically a short description of what the web page is about. Again, because of its prominent position, it helps the search engines to determine the relevancy of your web page to the search query.
Same as with the title, the meta-description is also displayed in a search query. It lets the searcher knows what to expect when they visit your page. Optimizing this part help the user decide whether they should click on your page or not.
The title and meta – description should be optimized for both search engines and users. An enticing title and meta description increases click-through rate that can also help rank your page higher.
Although I advocate that all sites should be optimizing their images, this can be especially true for visually-oriented sites, such as pictorial how-to tutorials and photography sites.
In short, optimizing an image is just a way of making sure that it displays well on devices of various sizes.
Alt-text is part of image optimization, and is great for accessibility: some people may have difficulty seeing, and they may rely on screen reader software. This software can read alt-text and tell that person what the image is about.
Yes, you guessed it: search engines can also read this alt-text. Search engines do not have eyes and cannot see what the image is. They rely on the alt text to know what the image is and using your target keyword and explaining what the image is helps your page and image get ranked. I’m sure you know that Google has an image search, so if your images are optimized, they could rank, thus opening up another avenue for visitors to find you.
In case you’re not sure, a URL is just the full address of a web page. (It’s sometimes called a link, which isn’t always the case.) If you’re on a laptop, it’s probably what you see in your browser’s address bar.
Anyway, it’s been known that it’s good to have shorter URLs (because they’d be easier to remember) and to have your main keywords in the URL of your page. Not only would that make sense for search engines, but from a searcher’s perspective, it’s more visually appealing.
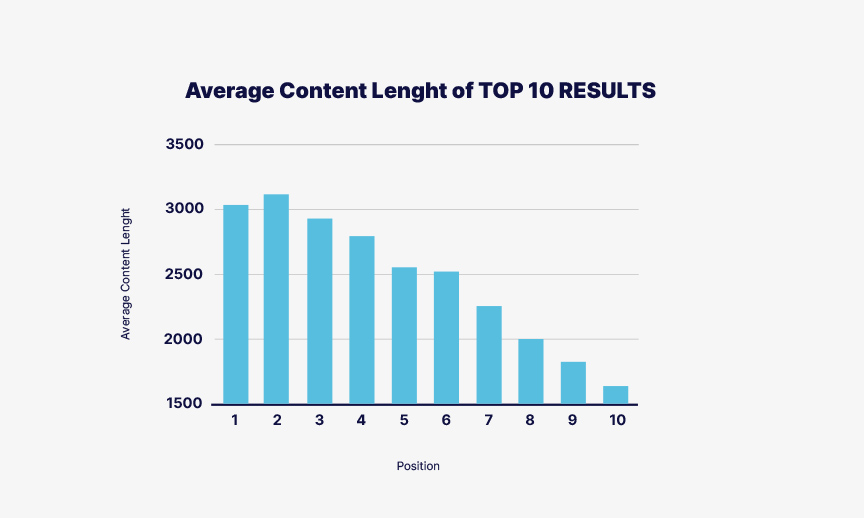
I think the simplest way I can describe this is to say that you want your content to be as thorough as possible.
The takeaway here is that you want the length of your content to be comparable to the length of the pages that rank for the keyword you want to rank for.
So, if you want to rank for a given keyword, do a search for that keyword. On the Google results page, go to each of the top 10 (or top 5) organic search results (not the sponsored/paid ones), and calculate the average word count of the pages you find.
You want your content to be around that word count.
If you’re in a video-oriented market or would like to rank your video content, just be sure it’s as thorough (or better, more thorough) and of a comparable length
Content quality is also considered. High quality piece of content that is relevant to the the search intent of users rank better than low quality content. Aim for relevant content to your keywords that are comprehensive. Avoid duplicate content. While duplicate content is not a penalty, there are filters for this and more often than not, the higher authority site is the one that ranks and lower quality sites that have duplicate content are filtered out of the Google search results.
Also, low quality content will cause a high bounce rate as this will not satisfy the intent of the user and they would just end up leaving the page and looking for answers or what they need elsewhere.
Having a content strategy for your website is also a good idea as this would help with the planning of what content your site will have and you could work on the internal linking of your pages. This would serve to keep users longer on your site and visiting other pages of your site also cause of the awesome content on your site.
Don’t let that term scare you. If your content is from a place of knowledge and authority, you’ll cover this.
Semantic saturation just means that search engines understand word associations. For example, if a document is about a school, the words classroom, teacher, and student are close associations. Another term that’s more known for this is LSI or latent semantic indexing. (We have an articles and tests on LSI that you can read about that gives you more details on this and why you should use LSI on your content)
When writing content on a particular topic, it’s natural to use some LSI terms. I encourage people to be comprehensive in their content, both ideologically and semantically as the more comprehensive your content is, the more LSI you get to use and the more that search engines can judge your topic and its relevancy to a search term based on your content. Comprehensive content can also rank for more keywords and your page can gain more SEO visibility.

If you’ve done Google searches for books, movies, and products, you may have seen little review stars by certain listings.
That’s likely due to something called Schema, which is a categorization system that webmasters can apply so that search engines can better categorize their site.
Schema may be a ranking factor because the easier you make it for the search engines to categorize your pages, the more likely your site will be found.

Internal links are simply links to other pages of the same site (or domain). Wikipedia is the epitome of internal links.
Internal links are great because they can help search engines (and users) navigate to other pages that are relevant to your article. They may be a ranking factor because links can be thought of as a form of currency, so a link from one page counts as a ‘vote’ for the page it’s linking to. Also, using an internal link anchor text that is relevant to what the page is about helps search robots determine that the particular page is about that topic.
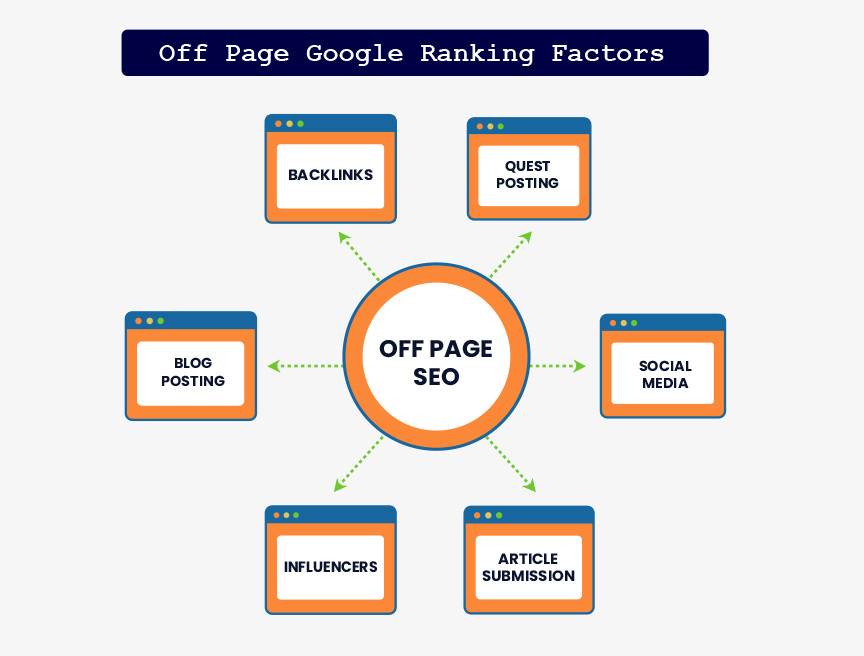
Off-page ranking factors can also be thought of as ‘off-site,’ or also, external. Here’s one that you don’t normally hear of…
Below, I’ll mention backlinks, but there’s something very obvious about backlinks: they’re easily manipulated.
But what isn’t as easily manipulated is traffic–real people–coming to a site from web 2.0/social media.
While I don’t think Google will come out and say this, it’s not a far-fetched statement: Android and Chrome can be great sources of data for Google. While Google may not be able to monitor the entire Internet, Android and Chrome are good reference points.
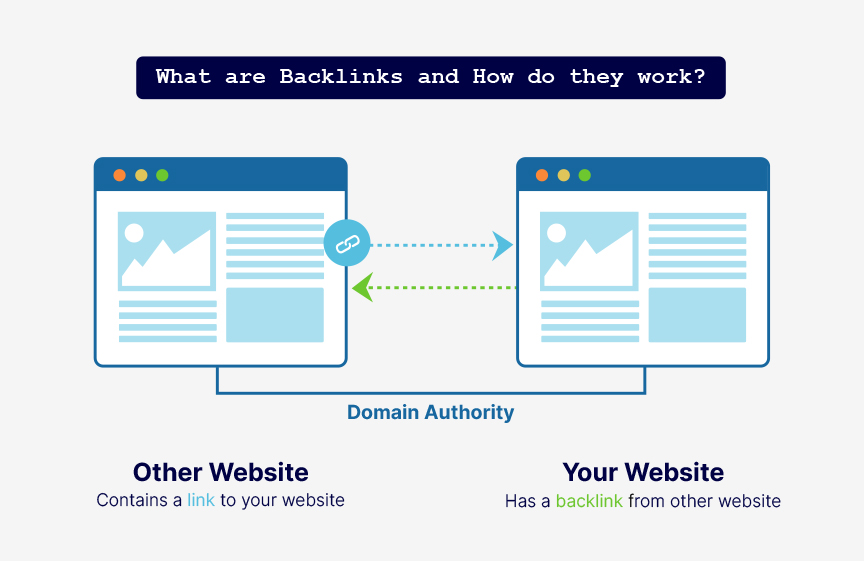
It’s been long known that backlinks from other sites–particularly well-reputed sites–are a strong ranking factor.
Backlinks, also known as inbound relevant links or are links from one website to another that Google considers as a positive vote from another site. This is because a site would only link to another who has valuable content. The more high quality inbound links a page has, the higher its chances of ranking in relevant search.
While this isn’t necessarily an exhaustive list, what I’ve listed here are some of the most important search ranking factors that I tend to focus on. And remember, you’re the most important ranking factor.
This is just a short run through of some ranking factors to help you rank in organic search and gain organic traffic to your site. We have more articles that delves into each factor further and provides things to do for your SEO checklist – technical seo, on-page SEO, off-page SEO. Check out our articles to help you come up with a SEO strategy, that would help you beat your competition and have a positive impact on your organic search rankings.
