
This week has been busy in the tech world with OpenAI’s release of GPT-4o (No OpenAI Search Engine!, yet) and Google I/O where we were shown a sneak peek of what is coming to search. Truly, what a time to be alive – tech advancement, wise. SEO wise, seems like the release of AI Overviews got everyone worried and scrambling on how these changes can affect their site’s traffic.
Check out this week’s notable news in the SEO space.
Google has announced that they have finally rolled out AI Overviews to the US and is set to roll it out in more countries soon.
AI Overviews provides answers to queries using Google’s Generative AI – Gemini. The responses are generated from a variety of sources, including web sources. It was introduced as a part of the Generative Search Experience in Search Labs last May 2023 and was tested to a subset of users in March 2024.
AI Overviews is not available for all searches. It only shows for queries that are more complex in nature, where the overview would provide more value.
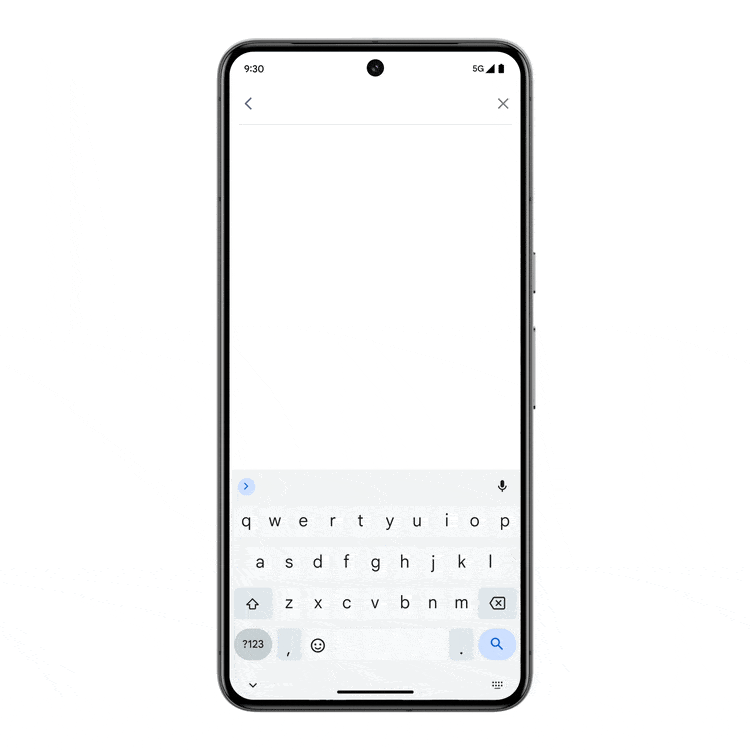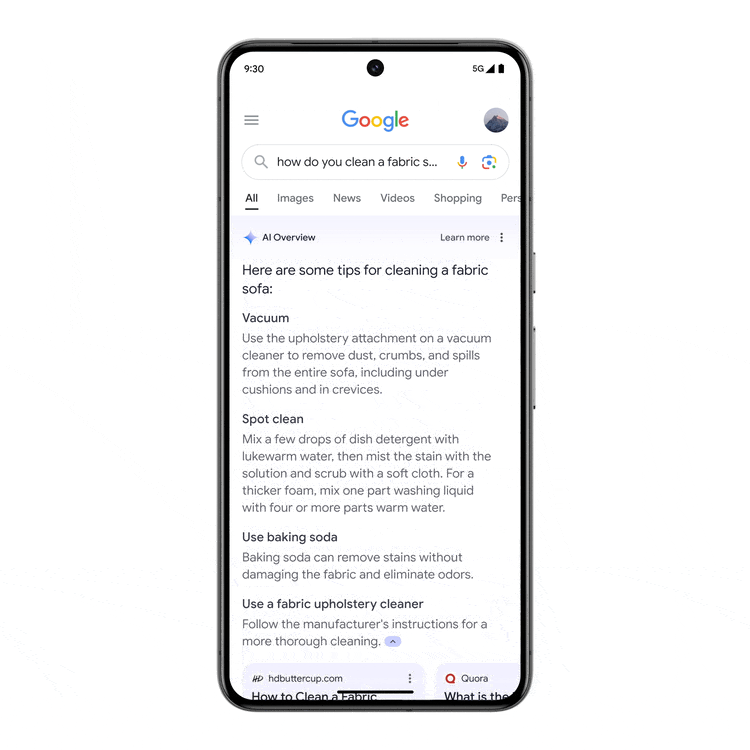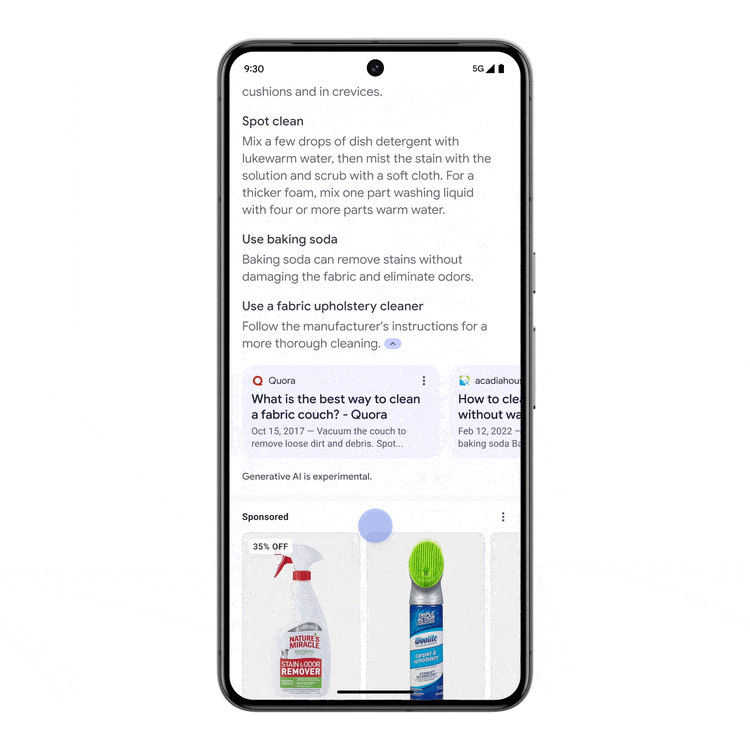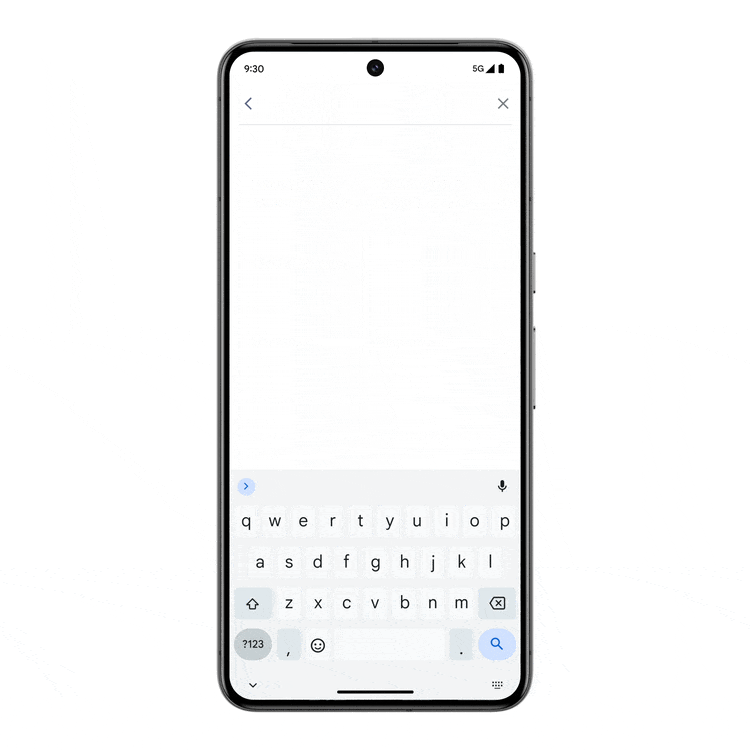
In the announcement, Liz Reid – Google‘s Head Of Search, mentioned that people have already used AI Overviews billions of times in Search Labs and that users like that they can get both a quick overview of a topic and links to learn more about it. Google has found that with AI Overviews, people use search more and are more satisfied with the results. They are visiting a greater diversity of websites for help with more complex questions.
She also mentioned that the links included in AI Overviews get more clicks than if the page had appeared as a traditional web listing for that query. As they expand this experience, they’ll continue to focus on sending valuable traffic to publishers and creators.
A lot of SEOs, publishers, website owners, creators, etc. have expressed concern about the release of AI Overviews as it may spell further loss of traffic to their sites since users can get what they are searching for directly in the Overviews section. As the feature continues to roll out to more and more users, we can only wait and see what effects it generates. It might be high time not to rely mainly on Search for traffic but to also explore different sources.
Google has announced that they are adding new features to Search Labs, thanks to their new Gemini model customized for Google Search. This new customized model brings together Gemini’s advanced capabilities – including multi-step reasons, planning, and multimodality – with what they call their “best-in-class” Search systems.
Here are the new features to be added to Search Labs:
Search Lab users will soon be able to adjust their AI Overview with options to simplify the language or break it down into more detail. This is helpful if you are new to a topic or just trying to simplify something in order to make it easier to understand. This would be available for English queries in the U.S.
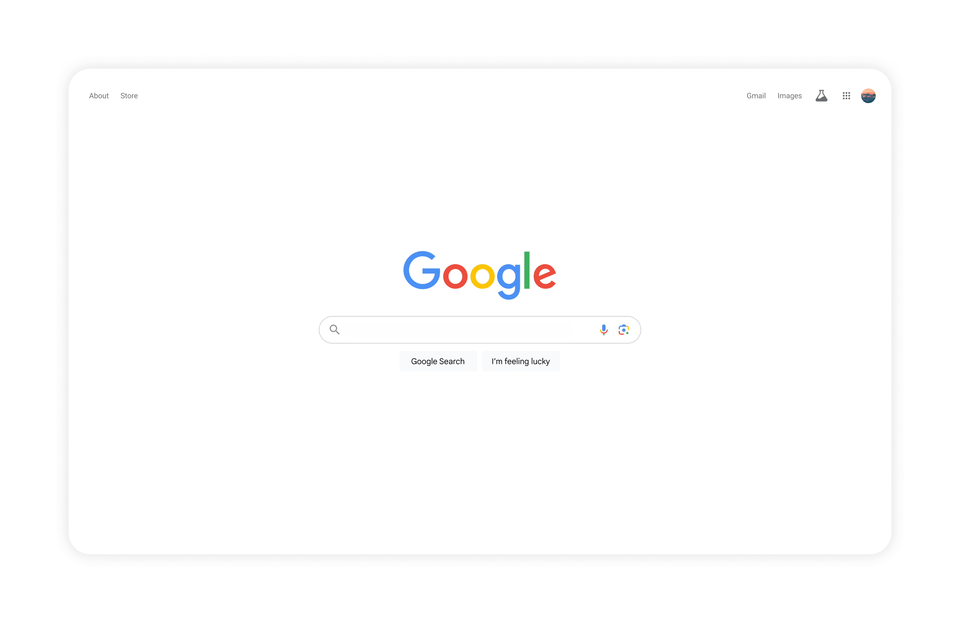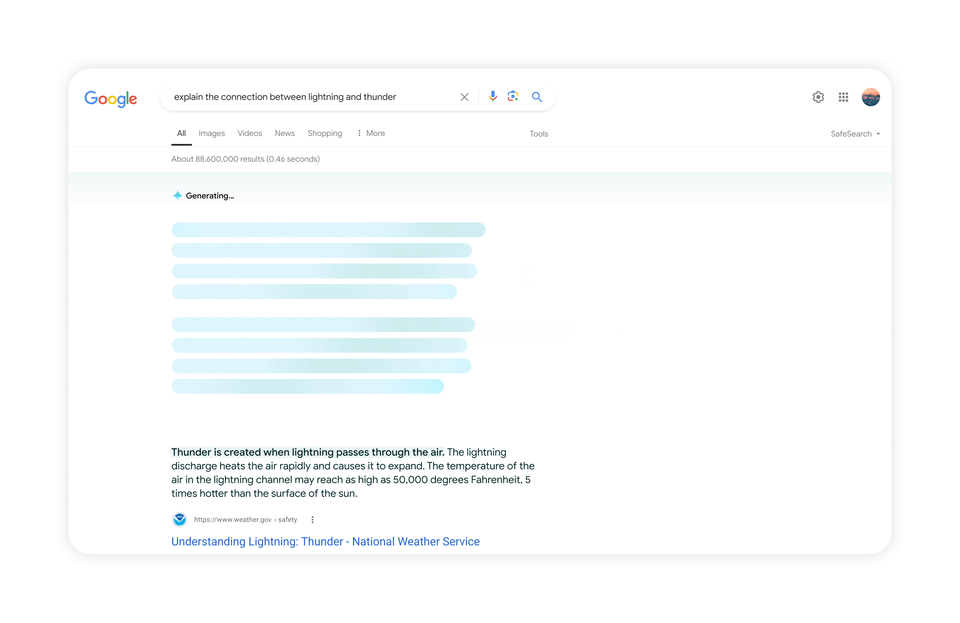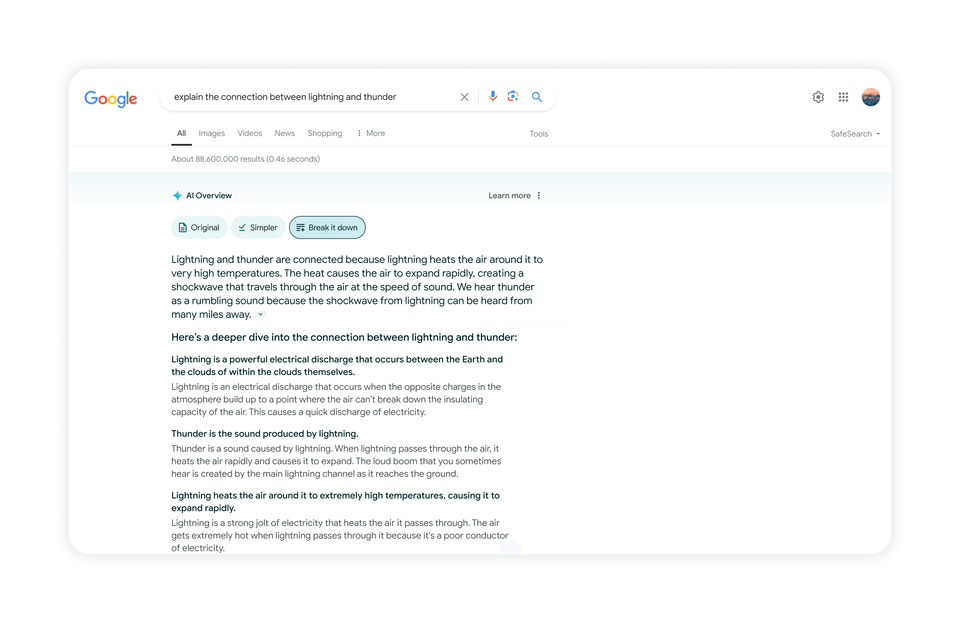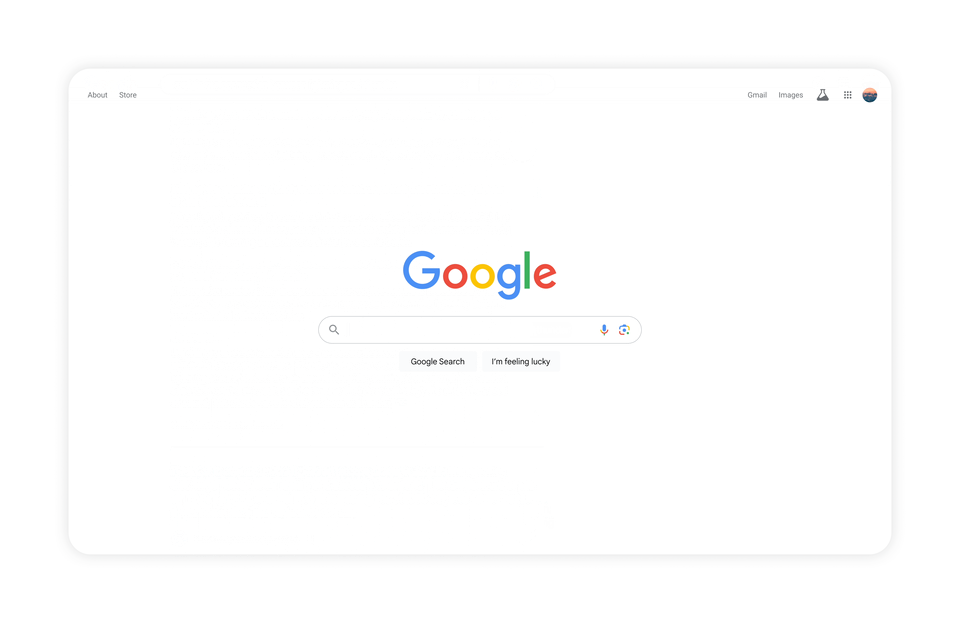
With the help of Google’s custom Gemini model’s multi-step reasoning capabilities, AI Overviews would be able to help with more complex questions. Rather than breaking questions into multiple searches, you can ask your most complex questions, with all the nuances and caveats you have in mind, all in one go.
For example, maybe you’re looking for a new yoga or pilates studio, and you want one that’s popular with locals, conveniently located for your commute, and also offers a discount for new members. With just one search, you’ll be able to ask something like “find the best yoga or pilates studios in Boston and show me details on their intro offers, and walking time from Beacon Hill.”
This is also coming soon to AI Overviews in Search Labs for English queries in the U.S.
Search will soon also be able to plan with you. With planning capabilities directly in Search, you can get help in creating plans for what you need – such as with meals and vacations. Search for something like “create a 3-day meal plan for a group that’s easy to prepare,” and you’ll get a starting point with a wide range of recipes from across the web. If you want to change anything, you can easily ask for whatever adjustments you need, like swapping dinner to a vegetarian dish. Just like that, Search will customize your meal plan. You’ll be able to quickly export your meal plan to Docs or Gmail.
This feature is now available in Search Labs in English in the US. Later this year, customization capabilities with more categories like parties, date night, and workouts will be added.
When looking for ideas, Search will use generative AI to brainstorm with you and create an AI-organized results page that makes it easy for you to explore. Results will be categorized under unique, AI-generated headlines, featuring a wide range of perspective and content types.
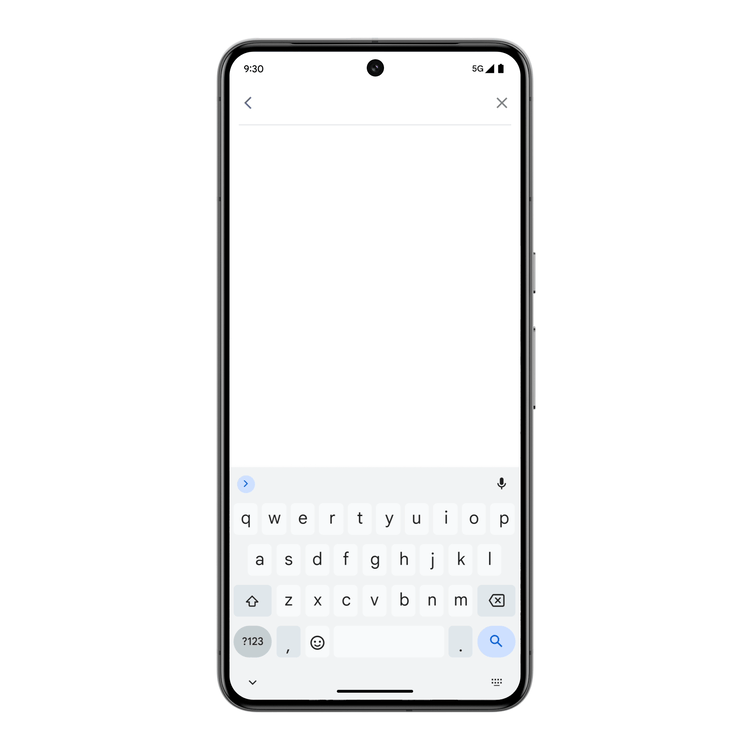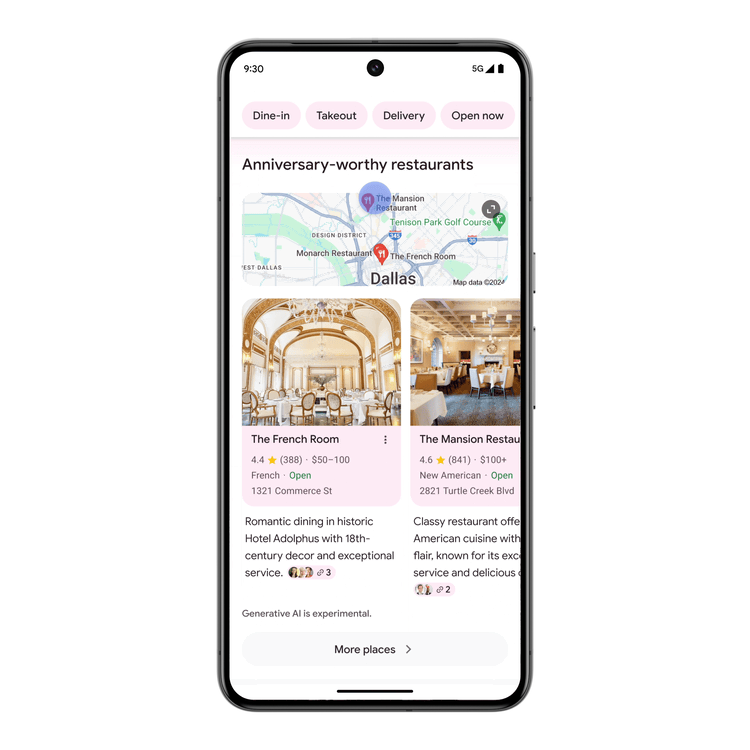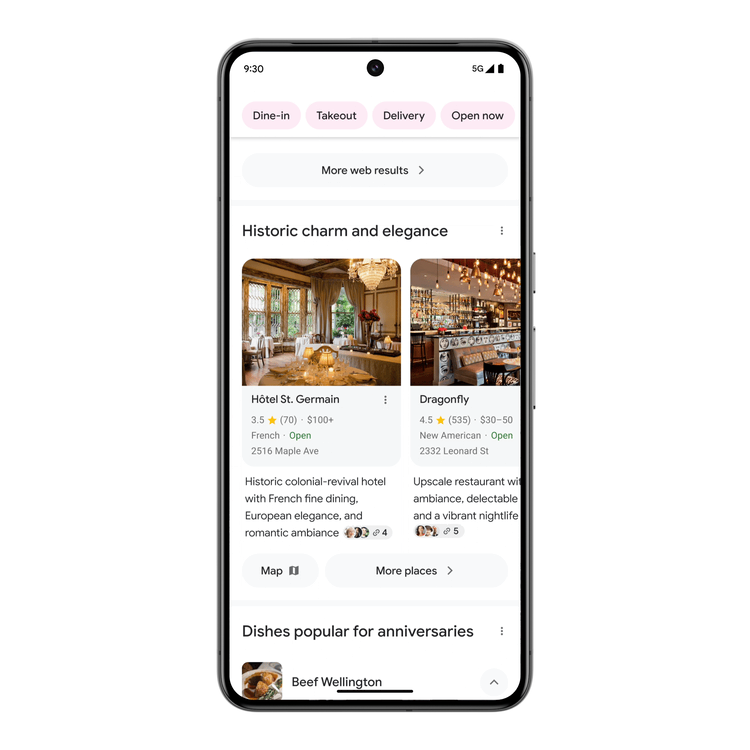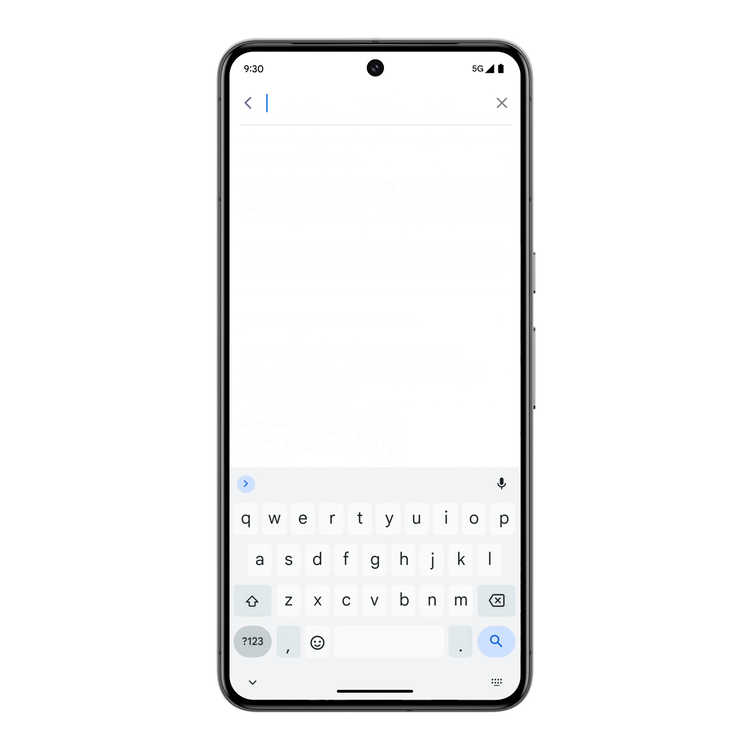
This will be available for English searches in the US when looking for inspiration – starting soon with dining and recipes, followed by movies, music, books, hotels, shopping, and more.
Visual search is taken to a whole new level, with the ability to ask questions with video. Maybe you bought a record player at a thrift shop, but it’s not working when you turn it on and the metal piece with the needle is drifting unexpectedly. Searching with video saves you the time and trouble of finding the right words to describe this issue, and you’ll get an AI Overview with steps and resources to troubleshoot.
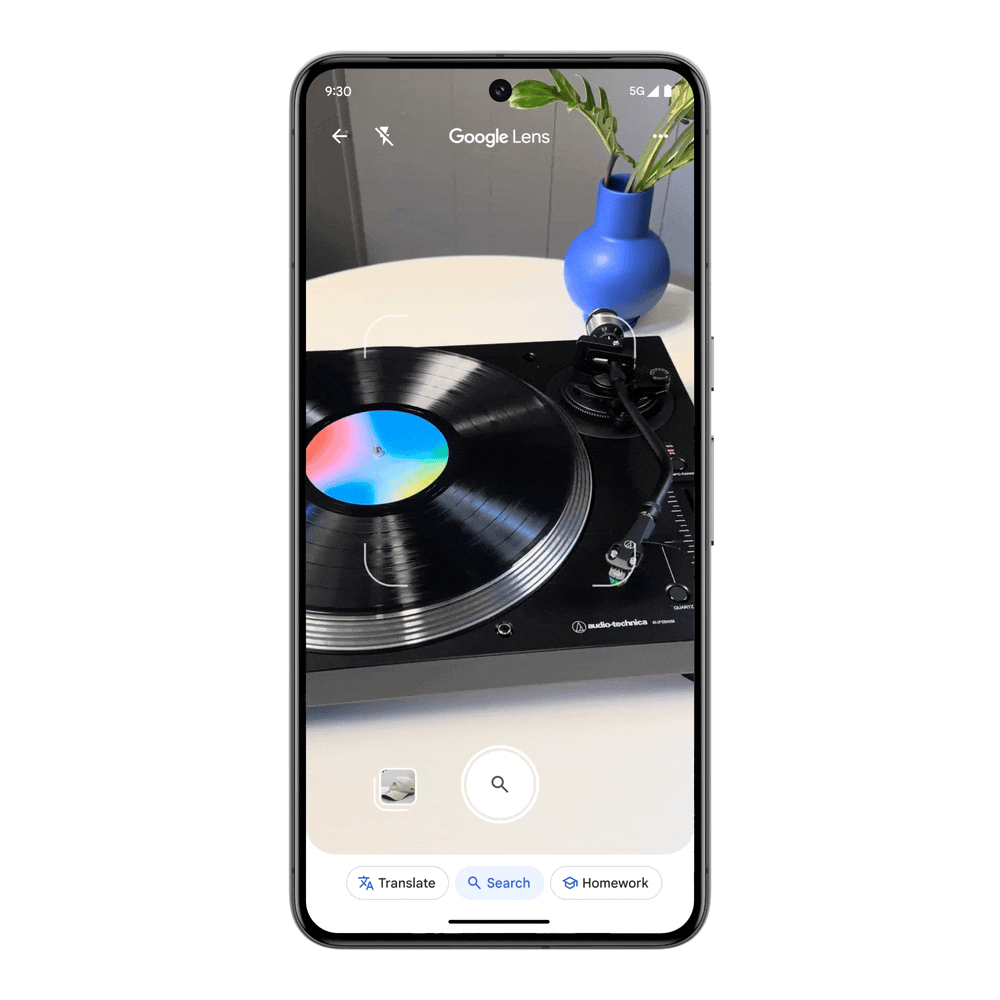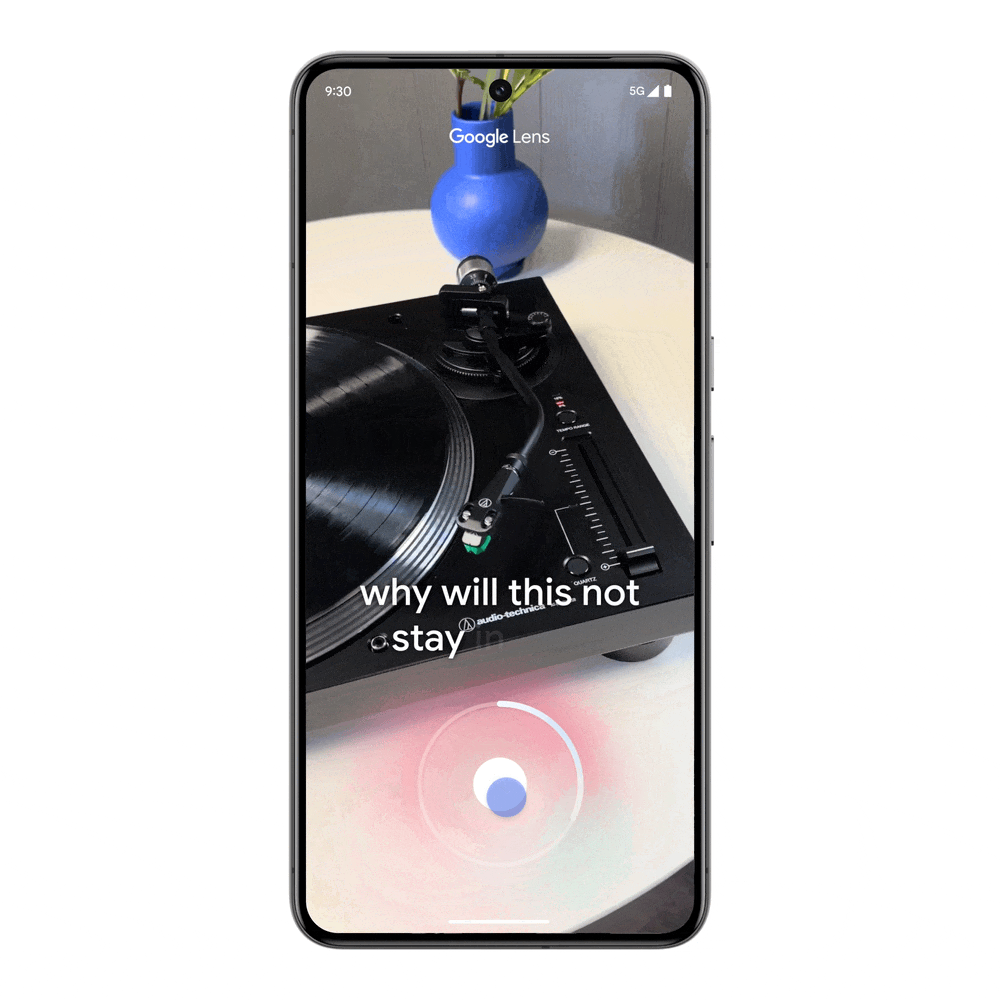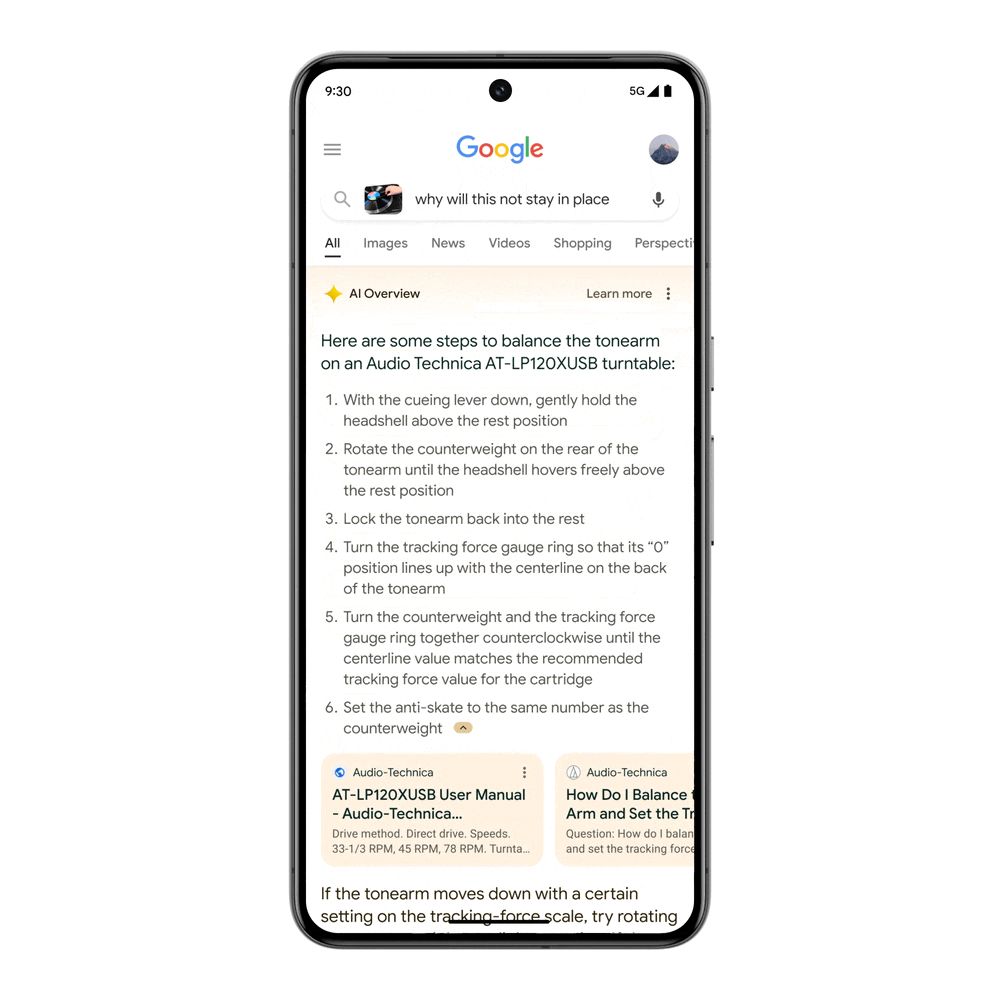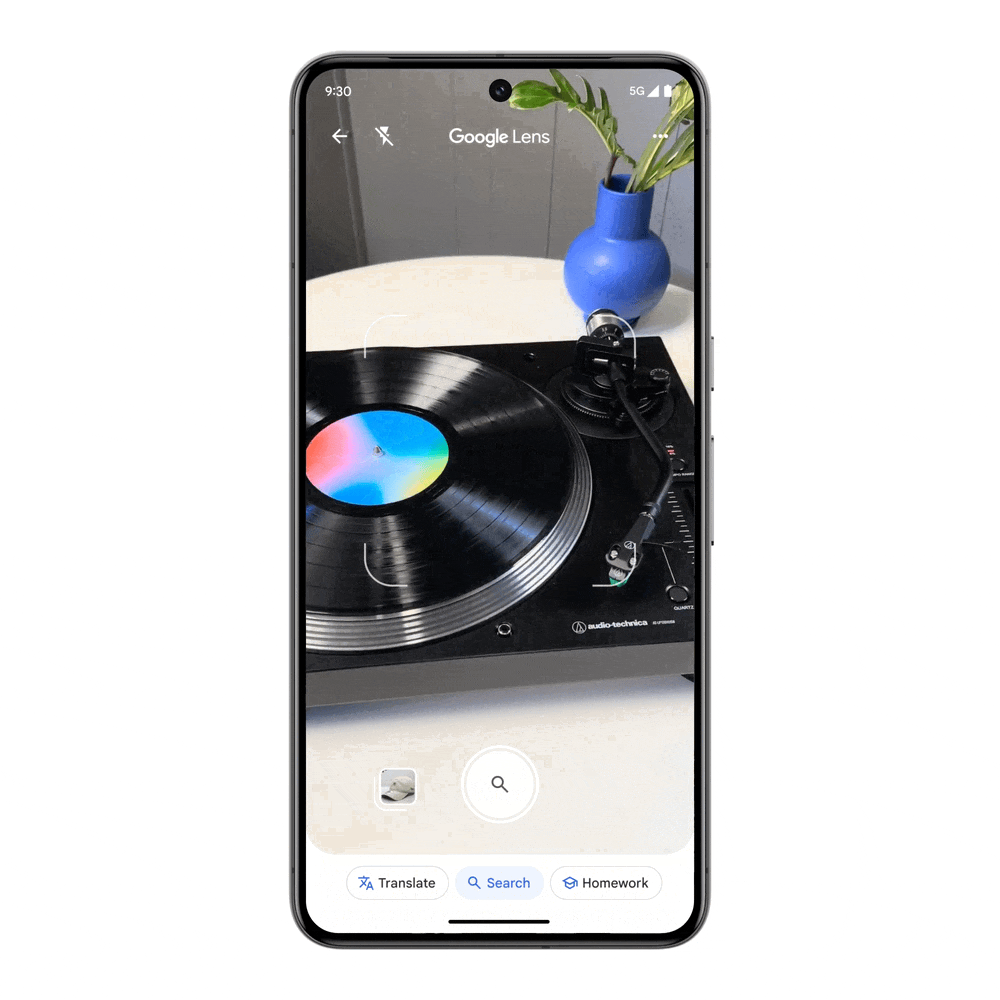
This feature will soon be available for Search Labs users in English in the US, and will expand to more regions.
Check out the full sneak peek video below –
Google’s Search Results Page has received a lot of updates over the years, from originally just featuring 10 text with a link to the site, to a search results page that includes images, videos, featured snippets, news, etc.
Different filters have also been added to sort results according to a searcher’s preference. A new one has recently been added, which is a filter for “Web” results only, for those who would only like to see those 10 text based links to sites. This filter removes images, videos, and other forms of search results and only displays the classic blue links.
Apparently, Danny Sullivan, Google’s Search Liaison is the one who championed the creation of the Web filter. He wrote on X: “Since I joined Google, I’ve just been a boy standing in front of the search group asking it to love a Web filter. So happy to see it’s arrived – congrats to the hard-working team on this project that through their own efforts made it a reality!”
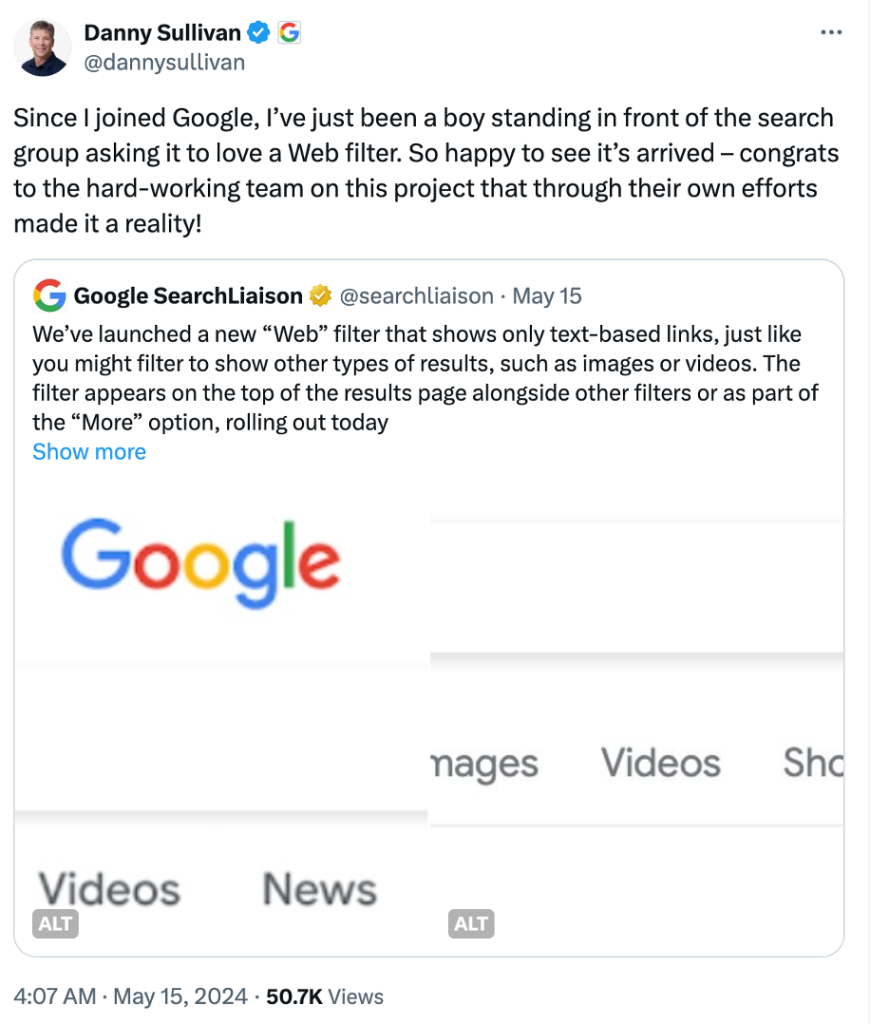
Sullivan added that the filter has been included after hearing from some that there are times when they would prefer to see just the links to web pages in their search results, such as if they’re looking for longer-form text documents, using a device with limited internet access, or those who just prefer text-based results shown separately from search features.
The “Web” filter can be accessed alongside the other filter options, on top of the search results page. Sometimes it appears beside the main filters shown, sometimes it appears only when clicking the “More” filter option.
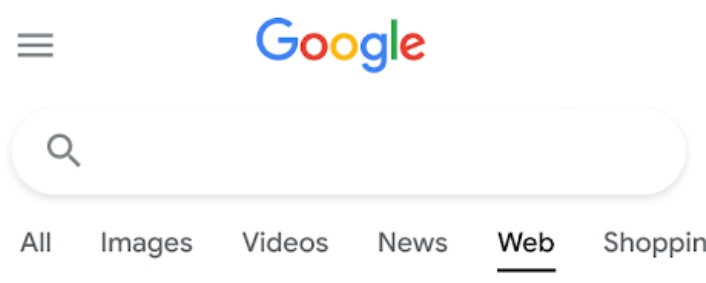
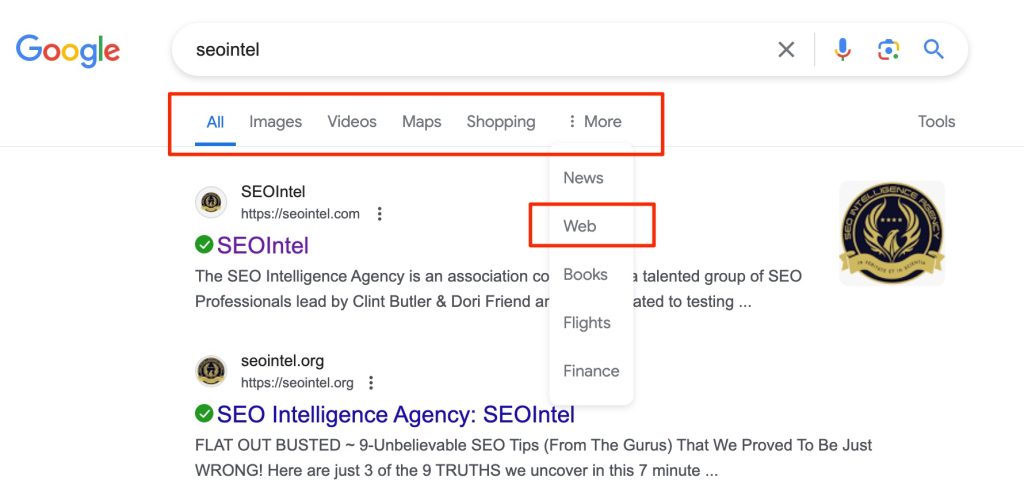
Sullivan added that on mobile, they tend to show all filters, including the new web one and users don’t need to go to “More” for it. On desktop, filters that seem most relevant are dynamically shown.
Search Engine Roundtable reports that Gary Illyes from Google has confirmed that they have suddenly deindexed a vast amount of URLs in February due to Google’s change of perception about a site. Gary said this at a SERP conference back in mid-April.
Here is the transcript:
“And in general, also the the general quality of the site, that can matter a lot of how many of these crawled but not indexed, you see in Search Console. If the number of these URLs is very high that could hint at a general quality issues. And I’ve seen that a lot uh since February, where suddenly we just decided that we are de-indexing a vast amount of URLs on a site just because the perception, or our perception of the site has changed.
Ah so after February there’s a possibility that things could have changed in Google Search Console as well because your perception not you personally but Google’s perception of the site has actually fundamentally changed.
So Search Console is using the data that Google indexing and Google ranking or Google serving produces right . And then it’s distilling that data into something that is intelligible by me or by you or by anyone else because the like the raw data this just doesn’t make any sense to to us as as humans.
And like one possibility is that when you see that number rising that Google’s perception of the site has changed. Like that could be one thing. But then there could it could also be that there was an error for example on the site and then it serve the same exact page to every single URL on the site. That could also be one of those one of the reasons that you see that number climbing. So yeah there could be many things in the vast majority of cases it’s a technical thing.”
Here is the video where Gary answers questions in the conference –
Google has added two new Google crawlers or Googlebots to their list of crawlers. These are the GoogleOther-Image and GoogleOther-Video crawlers. These are versions of GoogleOther that are optimized for fetching images and video bytes. The new crawlers were launched to better support crawling of binary data that may be used for research and development.

OpenAI launches GPT-4o, which is an iteration of the GPT-4 model. Same as the other models, the 4o model is also trained on enormous quantities of data to process queries, recognize patterns, and deliver helpful responses. The “o” in GPT-4o stands for “omni” as in omnimodal, which means it can accept input in any combination of text, image, audio, and can also produce output in these formats. All of these are processed in real-time, similar to human response time in conversations.
According to the release, GPT-4o is a step towards much more human-computer interaction.
Before GPT-4o, users could use Voice Mode to talk to ChatGPT. Voice Mode is a pipeline of three separate models: one simple model transcribes audio to text, GPT-3.5 or GPT-4 takes in text and outputs text, and a third simple model converts that text back to audio. This process means that the main source of intelligence, GPT-4, loses a lot of information—it can’t directly observe tone, multiple speakers, or background noises, and it can’t output laughter, singing, or express emotion.
With GPT-4o, OpenAI trained a single new model end-to-end across text, vision, and audio, meaning that all inputs and outputs are processed by the same neural network.
The faster response time and more natural conversational responses were apparent during the demo. It can be seen that it can comprehend human speech, respond in real time, show and recognize emotions, and joke around. The demonstration was able to show GPT-4os vision capabilities, conversational speech ability, and real-time translation skills, among others. It was mindblowing to see what it is capable of, much like a science-fiction movie on humanoid robots coming to life. Check out the video below:
GPT-4o is available to both free and paid users, with paid users having up to 5 times capacity limits to that of free users. The company will be rolling out features gradually to ensure they are used safely, starting it off with its text and image capabilities which is already available in ChatGPT.