
And just like that, we are in the final month of the year 2024. The November 2024 Core Update has finally finished rolling out and other than that, everything is quiet in the SEO space. Still busy and in holiday mode after Thanksgiving and Black Friday? Perhaps. Would the next couple of weeks be busy and will we see some big announcements before the year ends? We’ll see.
Check out this week’s notable news in SEO.
Google announced that the November 2024 Core update, which was released on November 11, is now complete (December 6). What was initially thought of as a two-week roll out took a total of 23 days, 13 hours to complete.
Though sites have reported drops in traffic and rank, this core update is not as impactful as compared to the March 2024 and August 2024 core updates.
When it was announced, Google has added that the update is designed to continue their work to improve the quality of their search results by showing more content that people find genuinely useful and less content that feels like it was made just to perform well on Search.
Experienced ranking drops and traffic drops from the update? Visit Google’s guidance on core updates for the next steps that you could take for recovery.
In the past weeks, people have been noticing that their Google Search Results are getting more personalized. For those in SEO, this can be an issue as what shows up can be different among different people, and tracking results from SEO efforts can be an issue.
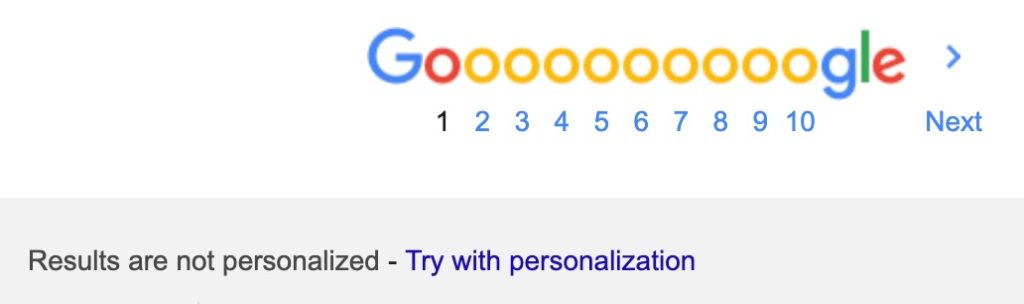
Seems like Google has heard the feedback from users as it has now added a new link at the bottom of the search results that provides users the option to turn off personalization and get the search results in its raw form.
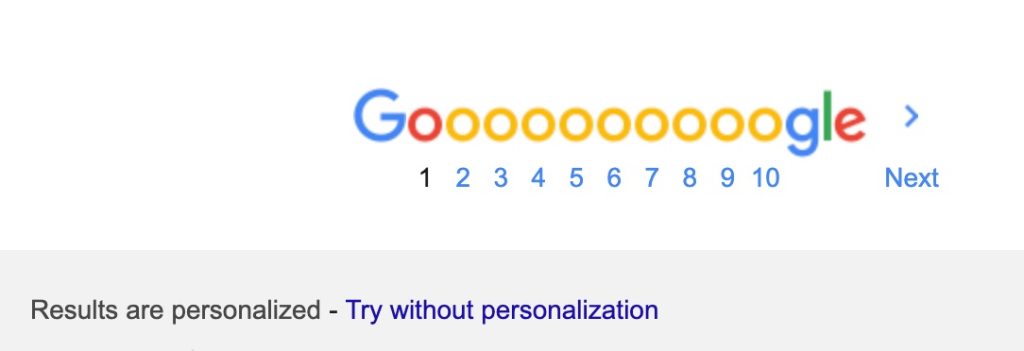
If the results are personalized, you can see “Results are personalized – Try without personalization”. If the results are not personalized, it will state that it is not personalized and in instances, you could choose to try personalized results.
SERoundtable reports that a Google spokesperson sent them the following statement on this added feature –
“This change makes it easier for people to get an accurate understanding of whether their results have been personalized, while also providing them with the opportunity to explore non-personalized results. We also make it easy for people to adjust their personalization settings at any time.”
In this week’s released episode of Google Search Central’s Search Lightning Talk, Martin Splitt of the Search Team talks about what a robots.txt file is and how it impacts a website’s indexability. He also covers how robots.txt interacts with robots meta tags, HTTP headers, and how to use the file to control search engine crawler’s access to your site.
The Robots.txt file is an html meta element that can be added you a site’s header. It can take a bunch of different things as its content. It can be set as noindex to keep a page out of Google’s search index. It can also get more granular and keep specific bots from indexing the page. Multiple things can also be specified in one tag. For example, if you do not want snippets and translations for the page.
An HTTP header can also be used instead of a meta tag. In such cases, the header would be called X-Robots and can contain the exact same values as the Robots meta tag.
These files are relatively simple and contain text in specific formats that many bots in the internet understand. It can be quite daunting to look at if you are not that familiar with it. If you are using a CMS or website builder, a plugin, a setting, or some other way is available to manage the robots.txt file content, so no need to worry much.
There are instances when people use both the robots.txt file and robots meta tags to stop a page from showing up in Google Search and having both does not work well. The problem with it is to see the robots meta tag or header, Googlebot would have to retrieve and access the page first. It cannot do that if you prevent Googlebot from doing it in robots.txt. The issue is that Google might find the link to that page somewhere and tries to crawl it, but finds out it is not allowed to crawl it. It knows the page exists but does not see what is on it – including the robots tag. So it might actually put it in the index, with limited information for the page due to being blocked in robots.txt.
To stop a page from getting into the Google index, use the robots meta tag or the X-Robots header, but do not disallow it in robots.txt.
Wondering how your robots.txt file influences Google? You can check out the robots.txt report in Search Console or you can also use this open-source robots.txt tester
Check out the full video below: