
After a stretch of relatively quiet weeks, search and AI came roaring back to life. Google officially rolled out the December 2025 Core Update, triggering noticeable volatility and renewing conversations around how rankings are evolving — especially alongside Google’s confirmation that smaller, unannounced core updates happen continuously.
At the same time, Search Console saw meaningful upgrades with new weekly and monthly views and the introduction of Social Channels reporting, giving site owners better ways to interpret performance.
Layer in Google’s global rollout of Preferred Sources, OpenAI’s “code red” release of GPT-5.2, and Google’s launch of its most advanced AI research agent yet — and this week feels less like routine updates and more like a reset moment for search and AI.
Read more on this week’s news roundup below:
Google has officially began rolling out the December 2025 Core Update to its search ranking systems. The update started on December 11, 2025, and Google says the rollout may take up to three weeks to complete.
Core updates are broad, foundational changes to Google’s ranking algorithms. Unlike targeted fixes (e.g., page speed or spam tweaks), core updates adjust how a wide range of factors are weighted together — essentially refining how Google assesses overall content relevance, quality, authority, and user satisfaction.
As with most major core updates, significant ranking volatility has been observed across the search ecosystem, with many SEOs and site owners noting fluctuations since early December. This follows a period of intense ranking shifts in early December, which some suspected was related to core changes.
Unlike smaller tweaks that happen quietly, this update is one of Google’s formally announced core updates — meaning it’s expected to impact rankings more broadly and noticeably across many verticals and query types.
Broad Quality Recalibration
Ranking Fluctuations Are Normal
Not a Penalty Per Se
While Google doesn’t disclose the precise mechanics of core updates, trends from early signals and industry analysis suggest:
Experts also note that sites with clear topical authority and strong internal linking structures tend to recover or improve more quickly after core changes.
Track Before You React
Early ranking volatility is expected — don’t jump to quick “fixes” mid-rollout. Wait until Google completes the update and trends stabilize before making major content or structural changes.
Monitor Trends, Not Daily Swings
Look for patterns — such as entire sections gaining or losing visibility — instead of reacting to isolated keyword movements.
Improve Content Where It Counts
Focus on producing helpful, original, experience-driven content that aligns with user intent, solves real problems, and adds value beyond what competitors offer.
Use Search Console & Tools
Check Search Console traffic and performance reports around the December 11 pivot date and beyond — comparing equivalent date ranges can help isolate the update’s impact.
The December 2025 Core Update is one of the major ranking shifts of the year, sitting alongside earlier core updates in March and June 2025. Early volatility is normal, and the full impact will only become clear once the rollout is complete and search behavior settles.
For site owners and SEO teams, the best strategy remains consistent: prioritize user-centered, deeply helpful content; maintain strong technical foundations; and let broader trends, not day-to-day ranking noise, guide your decisions.
Google has officially confirmed what many SEOs have long suspected: in addition to the widely announced core updates, Google regularly deploys smaller core updates that are not publicly announced. These updates are part of Google’s ongoing effort to improve search quality and relevance and can cause noticeable ranking changes — even when there is no official core update notification.
The confirmation came after questions from the SEO community about persistent ranking volatility occurring outside of major core update windows. Google clarified that while large, broad updates are announced to help site owners contextualize changes, smaller broad updates happen continuously and generally do not receive public announcements.
This clarification wasn’t shared casually or only via social media. Google formally added this explanation to its Core Updates documentation within the Search Developers guidelines.
The updated documentation now explicitly states that Google may release smaller core updates that are not announced, as part of its routine search system improvements. By placing this information directly in official documentation, Google is making it clear that unannounced core-level changes are a standard and expected part of how search evolves, not anomalies or experimental glitches.
For site owners and SEOs, this means ranking volatility can occur even when no core update banner appears on Google’s status dashboard — and that such movement does not automatically signal a problem or penalty.
Google uses the term “core update” for broad changes that affect how its ranking systems evaluate content overall. Large core updates — like those rolled out a few times per year — tend to be more impactful and therefore publicly announced.
Smaller core updates, on the other hand:
These updates can influence visibility across many sites, even if the impact feels subtler or more gradual than major core updates.
For years, SEOs have observed ranking fluctuations that didn’t align with known algorithm updates. Google’s confirmation now provides clarity: some of that volatility is intentional, driven by unannounced improvements to ranking systems.
This helps explain why:
Rather than viewing every fluctuation as a technical issue or penalty, it’s more accurate to see these movements as part of Google’s continuous recalibration process.
The existence of unannounced core updates reinforces several important best practices:
Focus on Long-Term Trends, Not Daily Noise
Short-term ranking changes are inevitable. What matters more is whether performance trends stabilize or improve over time.
Prioritize Content Quality and Usefulness
Because core updates — announced or not — evaluate content holistically, pages that are genuinely helpful, comprehensive, and aligned with user intent are more resilient to fluctuations.
Avoid Knee-Jerk Changes
Reacting too quickly to minor ranking drops can do more harm than good. It’s better to observe patterns across weeks rather than days.
Measure Beyond Rankings
With volatility becoming more constant, SEOs should track multiple indicators — impressions, engagement, conversions, and brand visibility — instead of relying solely on keyword positions.
Google has explained that announcing every incremental improvement would create unnecessary confusion. Smaller updates are part of routine maintenance, similar to behind-the-scenes tuning rather than headline changes.
Announcing only major core updates helps:
In other words, silence does not mean inactivity.
Google’s confirmation — now officially documented — changes how ranking volatility should be interpreted. Search is no longer shaped by occasional big events alone, but by a constant stream of smaller improvements that quietly reshape results over time.
For SEOs and site owners, the takeaway is clear: instead of chasing every fluctuation, invest in durable strategies — strong content, clear intent alignment, and consistent quality. In a world of both announced and unannounced core updates, stability comes from usefulness, not predictability.
Google has rolled out a highly requested update to Search Console’s Performance report — the ability to view traffic data not just by daily or 24-hour intervals, but now also weekly and monthly. This enhancement was announced at Search Central Live Zurich and is designed to give site owners, SEOs, and marketers clearer long-term insights into search performance trends.
Previously, Search Console’s Performance charts were limited mainly to daily data (or the recent 24-hour view). With this update, a new granularity selector appears in the date controls, letting you toggle between Daily, Weekly, and Monthly views depending on the level of trend detail you need.
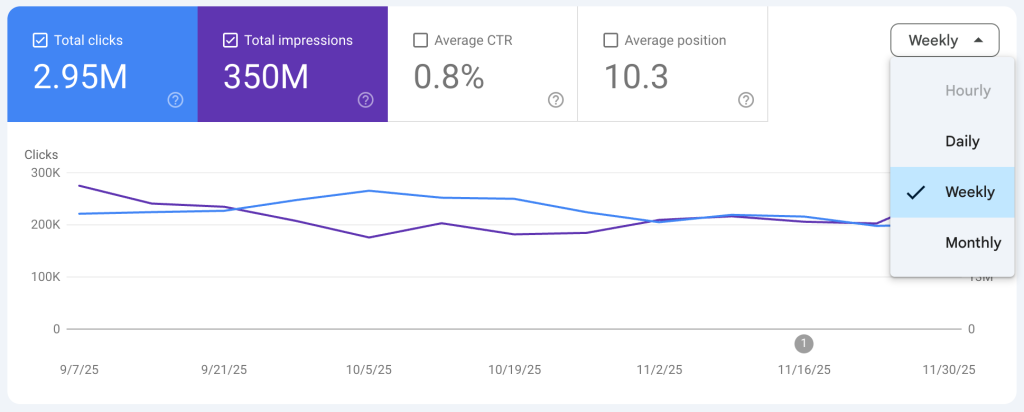
These new aggregation options apply not only to Search Results data but also to Google News and Discover performance reports, giving a more holistic view of how your content performs across surfaces.
Daily performance metrics are invaluable — but they can also be noisy, especially with natural fluctuations caused by weekends, holidays, small experiments, or minor algorithm changes. Weekly and monthly views smooth out that noise, making it easier to discern real momentum or decline without manual data manipulation.
For agencies and in-house teams alike, this means:
This change enhances how data is viewed — it does not change the underlying metrics or how Google calculates them. Daily and 24-hour views remain available, and no data is removed — you simply have more flexible lenses to interpret performance.
Also, the API and some advanced export tools may still default to daily granularity for now.
This seemingly simple update is one of the most impactful reporting upgrades to Search Console in recent memory. By giving SEOs and site owners multiple time-based perspectives, it’s now much easier to interpret genuine trends, allocate resources wisely, and communicate performance more clearly. If you’ve ever struggled to tell whether a traffic gain was meaningful or just a blip, weekly and monthly views will be a powerful new tool in your analytics toolkit.
Google has introduced a new Social Channels view in Search Console, giving site owners clearer insight into how social platforms contribute to their site’s visibility and traffic. This update allows publishers, SEOs, and marketers to see clicks and impressions attributed to social platforms directly within Search Console, rather than relying solely on external analytics tools.
The goal of this change is to help site owners better understand how social activity intersects with search performance — particularly as social platforms increasingly influence discovery, brand awareness, and follow-up searches.
The new Social Channels feature appears within the Performance reporting area and highlights traffic originating from major social platforms such as YouTube, X (Twitter), Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, LinkedIn, and Pinterest.
This data is presented separately from traditional Google Search traffic, giving a clearer picture of how social platforms contribute to overall site visibility. Metrics include:
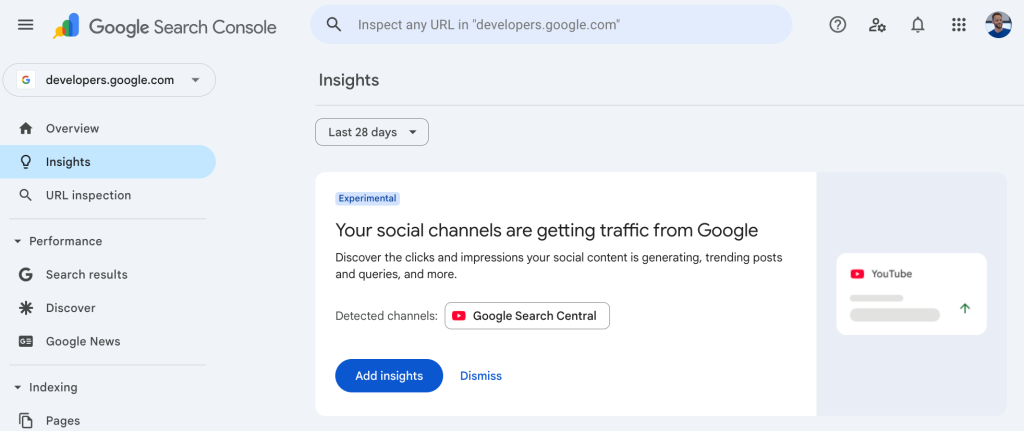
By centralizing this information, Search Console now offers a more holistic view of how users find your content beyond classic organic search.
Google acknowledges that discovery no longer happens through search alone. Social platforms increasingly influence:
By surfacing social channel performance directly in Search Console, Google is enabling site owners to connect social exposure with search demand. For example, a viral social post may not directly drive organic clicks, but it can increase branded searches — and this new view helps bridge that insight gap.
Better Cross-Channel Visibility
Instead of switching between analytics platforms, SEOs can now quickly assess which social networks are contributing to site visibility and engagement.
Improved Content Planning
Understanding which platforms drive impressions or clicks helps teams align:
Stronger Brand Measurement
Social Channels data complements branded vs. non-branded query tracking, offering better context for brand growth and awareness initiatives.
It’s important to note that:
Instead, this feature is designed to improve measurement and understanding, not ranking mechanics.
The addition of Social Channels in Search Console reflects a broader reality: search and social are increasingly interconnected. While rankings still matter, discovery now happens across multiple surfaces — and Google is giving site owners better tools to understand that journey. For SEOs and marketers alike, this update helps move performance analysis beyond search alone and toward a more complete view of how audiences find and engage with content.
Google has begun rolling out Preferred Sources globally, a feature designed to highlight trusted publishers and sources more prominently in search results. The update expands earlier, limited tests and reflects Google’s broader effort to surface high-quality, reliable content—especially for topics where accuracy, expertise, and trust matter most.
Preferred Sources is not a ranking “boost” in the traditional sense, but rather a visibility refinement that helps Google decide which sources to prioritize when presenting information-rich results, including summaries, panels, and AI-powered experiences.
Preferred Sources allow Google to identify and prioritize trusted domains for specific topics or content categories. When Google determines that a query benefits from authoritative sourcing, it may lean more heavily on these preferred publishers when generating result features.
In practice, this means:
The goal is to improve result quality—not by excluding others entirely, but by elevating sources with a proven track record of reliability.
Google has not published a checklist for becoming a Preferred Source, but the rollout aligns closely with long-standing quality principles, including:
These criteria echo Google’s E-E-A-T framework (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness), reinforcing that Preferred Sources are built through long-term quality, not short-term optimization tactics.
As search becomes more complex—particularly with AI summaries and conversational results—Google needs better ways to decide which sources to trust at scale. Preferred Sources help address challenges such as:
By prioritizing trusted publishers, Google can generate more accurate results while reducing exposure to unreliable sources.
Quality Over Volume
Being a Preferred Source is less about publishing more content and more about publishing better, more reliable content consistently.
Authority Takes Time
There’s no quick path to becoming a preferred source. Building authority requires sustained topical focus, credible authorship, and editorial discipline.
Visibility Beyond Blue Links
As Google surfaces information through summaries, AI responses, and enhanced result features, Preferred Sources may gain visibility even when users don’t click traditional links.
Preferred Sources works alongside existing ranking systems, not above them.
To align with how Preferred Sources works:
The global rollout of Preferred Sources signals a clear direction for search: trust and authority are becoming even more central to visibility. As Google relies more on curated sources to power AI-driven and information-heavy experiences, publishers who invest in credibility and expertise will be better positioned to stand out. In an era where not all content is treated equally, being trusted may matter as much as being relevant.
OpenAI has officially launched GPT-5.2, the latest iteration of its flagship language model series, designed to deliver significant performance and capability upgrades over previous versions. The release follows an internal “code red” directive from CEO Sam Altman earlier in December 2025, aimed at accelerating development in response to competitive pressure from rival models such as Google’s Gemini 3.
GPT-5.2 is positioned as a more capable, reliable, and productivity-focused AI system — with improvements spanning long-context understanding, reasoning, task complexity, coding, spreadsheets, presentations, and multimodal inputs — and is rolling out to users of ChatGPT and related enterprise tools.
According to OpenAI, GPT-5.2 is engineered to unlock “even more economic value” by enhancing core workflows and high-value tasks, especially for professional and enterprise users. Early reports detail the following improvements:
GPT-5.2 continues the GPT-5 series’ approach to adaptive model execution (previously introduced with GPT-5.1), striking a balance between fast responses and deeper expert reasoning when needed.
OpenAI highlights that GPT-5.2 achieves record-setting performance across multiple professional benchmarks — including GDPval, a metric designed to assess practical knowledge work across dozens of occupations — and is capable of outperforming human benchmarks in well-specified tasks at high efficiency and low cost.
GPT-5.2’s suite includes variants like:
These distinctions help match performance profiles to user needs and use cases.
The timing and urgency of GPT-5.2’s rollout are widely understood to be influenced by competitive pressures — particularly from Google’s Gemini 3 model, which recently topped several public benchmarks and was integrated into Google’s search and productivity ecosystem. Reports suggest that OpenAI’s internal “code red” was triggered to ensure GPT-5.2 narrowed capability gaps and strengthened OpenAI’s market position in generative AI.
While GPT-5.2 makes strides in professional and productivity tasks, its arrival underscores how the AI model landscape has become intensely competitive, with multiple organizations vying to lead in business integration, reasoning strength, and multimodal capabilities.
GPT-5.2 is being rolled out gradually across platforms, beginning with paid subscribers and enterprise users on ChatGPT, and is also being integrated into tools such as GitHub Copilot where it can be selected for coding assistance and workflow augmentation.
Developers and organizations with API access will find GPT-5.2 available alongside existing model options, allowing flexible deployment and experimentation across domains ranging from research and analysis to automation and content generation.
GPT-5.2 represents more than an incremental upgrade — it’s a strategic pivot designed to address both competitive pressures and evolving user needs in complex work environments. Its improved reasoning, tool capability, and long-context comprehension make it especially relevant to:
In a landscape where AI models increasingly shape productivity and innovation, GPT-5.2 aims to keep OpenAI competitive across enterprise, professional, and creative use cases.
With the release of GPT-5.2, OpenAI is staking a claim in the next phase of AI evolution — one focused not just on conversation or creativity, but on actionable intelligence that drives real-world work results. Whether used to automate complex tasks, power advanced applications, or fuel enterprise solutions, GPT-5.2 stands as a milestone in the ongoing AI race.
On December 11, 2025, the same day OpenAI launched GPT-5.2, Google released what it’s calling its deepest AI research agent yet — a powerful new extension of its Gemini family built on the Gemini 3 Pro foundation model. The rollout marks Google’s latest push into agentic, research-oriented AI systems, designed to handle sustained, complex reasoning tasks and provide high-quality research output at scale.
Unlike typical conversational chatbots, this new “Deep Research” agent can be embedded by developers into applications through Google’s Interactions API, allowing third-party apps to leverage Google’s most advanced reasoning capabilities directly. It’s tailored to tackle multi-step research workflows that involve deep context, multiple tools, and longer timelines than standard question-answer sessions.
Built for Deep, Multi-Step Reasoning
According to reporting, the agent is capable of handling extended research tasks, far beyond simple prompts — including multi-hour or multi-stage investigations that resemble human research workflows. Its architecture is designed to integrate reasoning with retrieval and analysis, making it suitable for tasks like due diligence, scientific reporting, or summarizing extensive documents.
Embeddable via the Interactions API
A key differentiator of this release is the Interactions API, which lets developers embed the agent’s capabilities into external apps — effectively giving software its own deep research engine. This opens the door for specialized industry tools, analytics platforms, and enterprise systems to leverage advanced AI reasoning without building it from scratch.
Built on Gemini 3 Pro
The “Deep Research” agent is powered by Gemini 3 Pro, Google’s most advanced model as of late 2025 — the same technology that’s being deployed widely in AI Mode and advanced reasoning contexts. This gives it broad language and multimodal understanding as well as improved reliability and depth in complex domains.
New Tier of AI Research Capability
Google’s deep research agent represents a shift from general conversational models toward AI that can conduct investigations at scale and with depth — a capability that’s increasingly useful for enterprise analytics, academic work, and professional knowledge tasks.
Strategic Timing in the AI Competition
The simultaneous timing with OpenAI’s release of GPT-5.2 underscores how competitive the AI landscape has become. While OpenAI’s new model focuses on broad improvements in reasoning, productivity, and professional workflows, Google’s deep research agent emphasizes specialized, high-context research competencies. This divergence highlights a broader trend where AI platforms are optimizing different parts of the intelligence landscape — general productivity on one hand, and deep analytical power on the other.
Implications for Developers and Enterprises
This could accelerate the adoption of AI in fields where deep, expert-level inquiry is needed — such as legal research, scientific literature synthesis, financial analysis, and competitive intelligence.
While initial details focus on embedding and advanced reasoning, future iterations of this research agent may expand into integrated agentic tasks across:
The launch also raises questions about how Google will balance depth and accuracy — particularly in highly technical domains — and how it will compete with similar efforts from OpenAI and other AI labs.
Google’s newest deep research agent represents a significant evolution in how AI systems can support extended, structured, and multi-step reasoning tasks. By enabling developers to embed this capability and tapping Gemini 3 Pro’s advanced model architecture, Google is pushing beyond simple conversational AI into tools that resemble autonomous research assistants. In an era of intensifying competition with OpenAI — highlighted by the near-simultaneous release of GPT-5.2 — this launch signals that the future of AI will be shaped not just by breadth of capability, but by depth of reasoning and integration.
What stands out this week isn’t just the volume of updates, but the direction they point to: search systems becoming more dynamic, AI models accelerating faster, and visibility being shaped by trust, context, and continuous change rather than isolated updates. With core updates rolling out — both announced and unannounced — and AI capabilities expanding on both the Google and OpenAI fronts, staying grounded in long-term quality and adaptability matters more than reacting to daily fluctuations. As the dust settles from a busy week, the takeaway is clear: search isn’t slowing down — it’s evolving in layers, and those who understand the bigger picture will be best positioned to navigate what comes next.