
Having issues with some pages of your site not being crawled and indexed? Perhaps it’s time to look into your site’s pages, trim content, and search for issues that might be affecting your site’s crawl budget.
But first, what is crawl budget, why is it important, can you increase your site’s crawl budget, what are steps that can be done to improve your site’s crawl budget? We discuss all these in this article.

Crawl budget is the number of pages crawled by search engine crawlers, spiders, and robots on a website, within a given timeframe.
The crawl budget is calculated by search engines based on the crawl limit, like how frequently they can crawl without causing issues and crawl demand, which means how frequently they’d like to crawl a site (crawl frequency).
If you waste your crawl budget, search engines will be unable to get an efficient crawling for your site and its pages, resulting in poor SEO performance.
When spiders encounter crawl issues every time, the crawl rate may be limited during the crawl process.
To avoid crawl issues, ensure crawl efficiency in order to maximize your site’s crawl budget.
Search engines don’t have unlimited resources to crawl millions of websites and all of their pages. As a result, they have set a method to prioritize their crawling effort through assigning an average crawl budget for each website that they come across.
If Google does not index a page, it will not rank for anything.
If the number of pages on your site exceeds the crawl budget, you will have pages that aren’t crawled and aren’t indexed.
However, the vast majority of websites do not need to be concerned about the crawl budget. Google is extremely effective at finding and indexing pages.
However, there are a few instances where you should consider when it comes to average crawl budget:
The process of assisting Googlebot and other search engines in crawling and indexing more of your important content is known as crawl budget optimization.
There are three main ways to accomplish this:
Following that, here are some easy ways to increase your site’s crawl budget.
The goal of optimizing your crawl budget is to ensure that no crawl budget is wasted. This is done by fixing the root causes of crawl budget waste.
Here are some reasons for wasted crawl budget:
To improve your crawl budget here are the best practices you need to follow:

One thing you need to do is to improve the page speed of your site, this may result in Googlebot or search engine bots crawling more of your site’s URLs. In fact, Google claims that speeding up a site improves user experience while also increasing the crawl rate.
To put it another way, slow-load time of pages waste Googlebot’s time, however, if your pages load quickly, Googlebot will have more time to visit and index your pages.
Note that pages with a high number of external and internal links pointing to them are prioritized by Googlebot, so learn what pages to prioritize.

Yes, thou shall not forget this part where you should ideally have backlinks pointing to every single page on your site. However, in most cases, this is not feasible, that’s why internal linking is so important.
Internal links direct Googlebot to all of the pages on your website that you want to be indexed. A good internal linking structure also helps Google understand your content better and how each pages relate to each other.
Check out our internal linking guide for tips on how you can effectively internal link your pages.
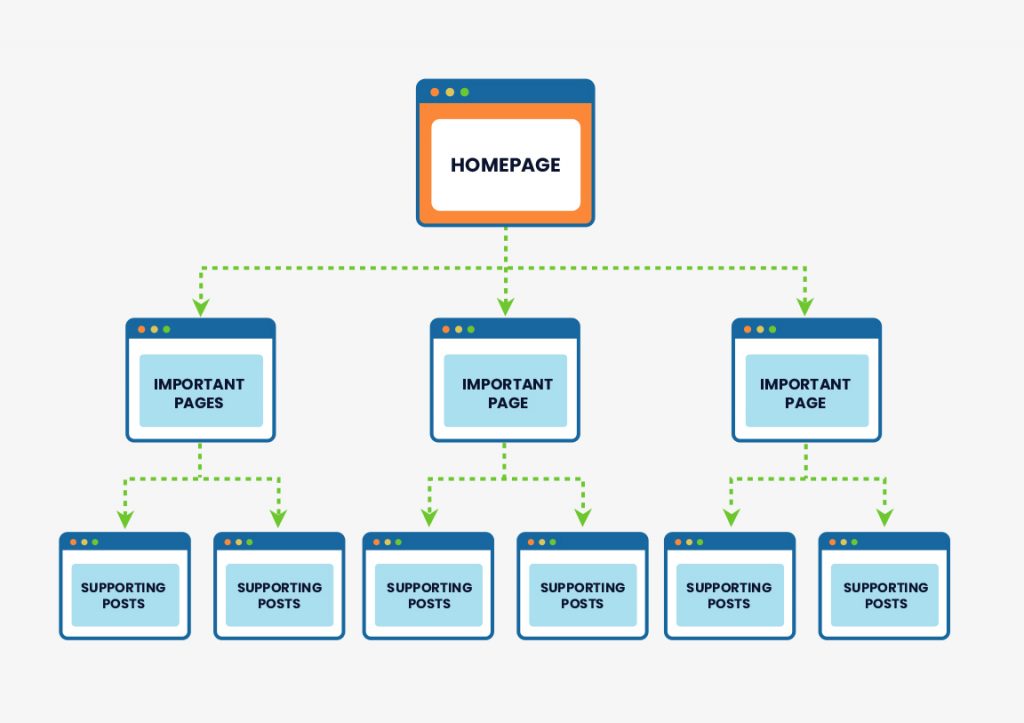
According to Google, “More popular URLs on the Internet are crawled more frequently to keep them fresher in our index,” so in the world of Google, popularity equals link authority, a reason why you should use a flat website architecture on your website. A flat architecture arranges things so that all of your site’s pages receive some link authority.
Check out our website architecture article on tips on how to set up an SEO-friendly website architecture.
Orphan pages are pages that have no internal or external links pointing to them. They are considered orphans because it seems like you’re abandoning them.

Google will have a difficult time locating orphan pages. So if you want to get the most out of your crawl budget, make sure that every page on your site has at least one internal link pointing to it.
Of course, limiting duplicate content is a good idea for a variety of reasons.
Duplicate content, it turns out, can deplete your crawl budget. This is due to Google’s desire to avoid wasting resources by indexing multiple pages with the same content. As a result, ensure that all of your site’s pages contain unique, high-quality content.
It is said that this is difficult for a site with 10,000+ pages, especially for e-commerce sites that can have products in multiple variations. However, it is required if you want to get the most out of your crawl budget.
According to Matt Cutts, Google’s former head of the Google webspam team, the most straightforward way to think about it is that the number of pages we crawl is roughly proportional to your PageRank. So if your root page has a lot of incoming links, they’ll definitely crawl it. Then your root page may link to other pages, which will gain PageRank and be crawled as well. PageRank, on the other hand, tends to decline as you go deeper into your site.
Even though Google has stopped publicly updating PageRank values for pages, we believe PageRank is still used in their algorithms. Because PageRank is a misunderstood and perplexing term, we can use the term page authority instead. Matt Cutts basically said that there’s a pretty strong relationship between page authority and crawl budget (as simple as that).
To increase your website’s crawl budget, you must first increase your website’s authority. A large part of this is accomplished by obtaining more links from external websites.
Crawl limit, also known as crawl host load, is determined by a variety of factors including the website’s condition and hosting capabilities. Search engine crawlers are configured to avoid overloading a web server.
The crawl budget will be reduced if your website returns server errors or if the requested URLs time out frequently. Similarly, if your website is hosted on a shared hosting platform, the crawl limit will be lower because you must share your crawl budget with other websites.
The crawl budget is more than a technical consideration, it’s a business decision. Utilizing these optimizations to a site with millions of pages can provide a plethora of opportunities — not only for your crawl budget but also for your site’s traffic and revenue. This is due to the SEO funnel principle which states that improvements in the crawl phase have downstream benefits in the ranking, traffic, and revenue phases, which your stakeholders will undoubtedly appreciate.