In a previous article, you have learned about keywords and key phrases that are usually entered on a search bar whenever we search something online. We even discussed how to create relevant content and the impact of organic traffic to your website and search rankings. So today, to further help you enhance the rank of your website and to get better conversions, we will talk about Semantic SEO, what it is, how semantic search works, and why it is important in search engine optimization.
Semantic SEO is a type of technical SEO that focuses on determining search intent and responding to any user queries may have. Semantic search engine optimization entails optimizing material for entities and subjects, as a whole. A page about entities provides information on those entities’ properties (entity recognition) such as facts that describe them and IDs that can be used to learn more about them.
The following elements can be found on a semantic search engine results page: Knowledge Panel, Entity carousels in the search results, Featured snippets that may provide information on the entities in a query, the “People also ask” questions that may be similar to the featured snippet replies, entities that are related, and more.
Are you still confused why we are discussing this stuff? Read this piece of content further to better understand semantic relevance and how it works.
Search Intent is determined by a number of criteria including the user’s location and previous behavior. This personalizes the search by building links between the words in the query and making the experience relevant to the user.
It also includes semantic search which functions as an additional layer to the search engine algorithm, processing information to determine context. To do this, search engines such as Google go through five phases to interpret the material semantically. These five phases are:
Yes! Google employs semantic approaches in order to improve its search formula and increase customer satisfaction.
To give the best SERP results and improve the user experience, Google employs artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. They’re also necessary for an effective semantic search. As a result, Google’s algorithms are updated on a regular basis.
There are three semantic search upgrades from Google:
Hummingbird interprets the meaning of distinct terms in a query to comprehend the context and return results that are relevant to the searcher’s intent.

Rankbrain is a machine learning system that recognizes the meaning of searches and returns relevant search results. It’s a component of the Hummingbird algorithm that also serves as a ranking element.
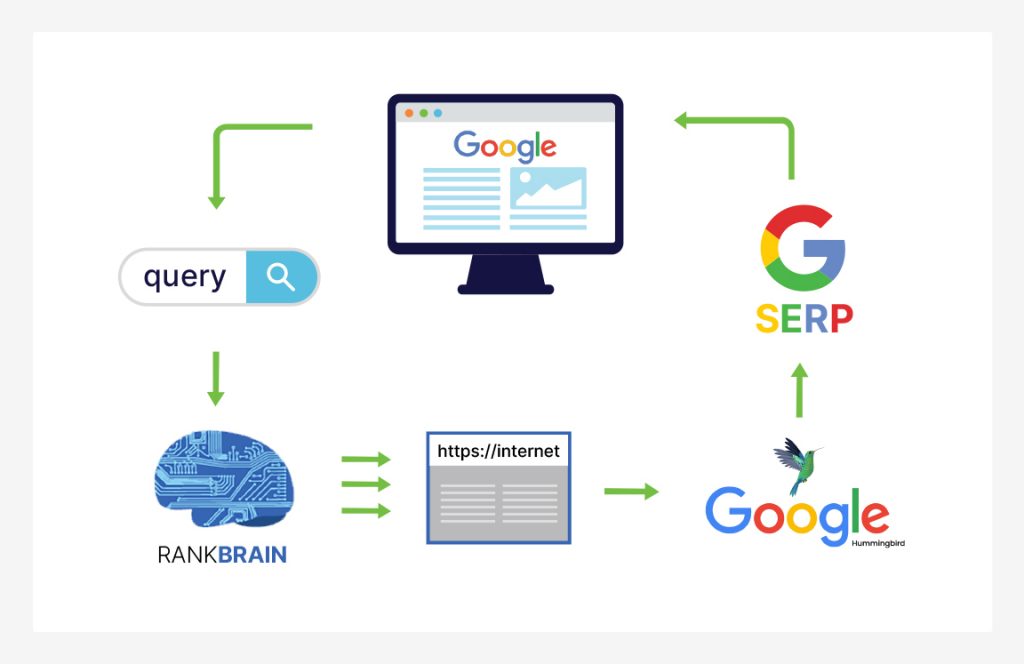
BERT makes use of natural language processing (NLP) technology to better understand search queries, parse text, and find relationships between words, phrases, other entities in human language and perception.
All of these changes are intended to improve the computer’s comprehension of the context surrounding search requests. It’s a machine that analyzes words and intent in great detail.
Those are just three of the algorithms used by Google for Semantic search. Check out this news article on How Artificial Intelligence Powers Google Search for more details on some of these AI algorithms.

Just like any other things and terms related to SEO, digital marketers need to better understand the importance of semantic search and why we are talking about it, especially if it involves your content strategy.
If you want to create pieces of content for SEO, Semantic SEO helps you in a larger purpose. Pages that employ this SEO method typically rank higher in search results and provide consumers with more in-depth material.
Google aims to present consumers with the most useful and valuable content possible and using Semantic SEO increases the likelihood that your content will be recognized as such. In addition, considering Google’s E-A-T principles also aids in the creation of high-quality content.
Although semantic content optimization is one of the most effective SEO approaches, the ultimate goal is to develop content that is optimized for consumers and not only search engines.
Because Semantic SEO is built on broader subject research, the key to this on-page SEO technique is mixing several semantically relevant keywords around your target topic.
Semantic keyword grouping allows you to expand the number of keywords for which your page can rank for. It also means you’ll have a better chance of getting more organic visitors.
However, do not mix this strategy with keyword stuffing, which might harm your SEO performance. Avoid a semantic chasm by naturally using keywords that are relevant to the context of your page.
Google and other search engines already rate pages for several keywords. Google can readily find subject synonyms and related terms on your page since it employs semantic analysis.
You should include semantic keywords in your title, headings, meta description, and body, as long as they fit into your content and don’t interfere with readability.
You might choose a keyword, include it in your title tags/descriptions/article titles, headers, and text, and then try to rank for it in the old days of SEO. However, as semantic search has progressed, the game has become more difficult to play, particularly for webmasters.
Concentrate on the topic and keywords that are used in your content, rather than gathering a vast number of keywords. Make a concerted effort to expand on this. Don’t forget about appropriate and on-topic internal linking opportunities and content structuring.
If you own the website, you may have observed that you have little control over the queries that are being entered into search engines or even how search engine algorithms rank our content. However, you have control over what goes into the search engine algorithms (input) and thus, you can tweak the rankings (output) by making sure that the search engine algorithms get the best data available from your website. Understanding semantics can help you with this.
You can divide your effort into two steps to successfully use semantic SEO: the content generation stage and the optimization stage.
The first stage consists of selecting a topic based on the user’s purpose, compiling a list of relevant keywords, and putting together the content structure.
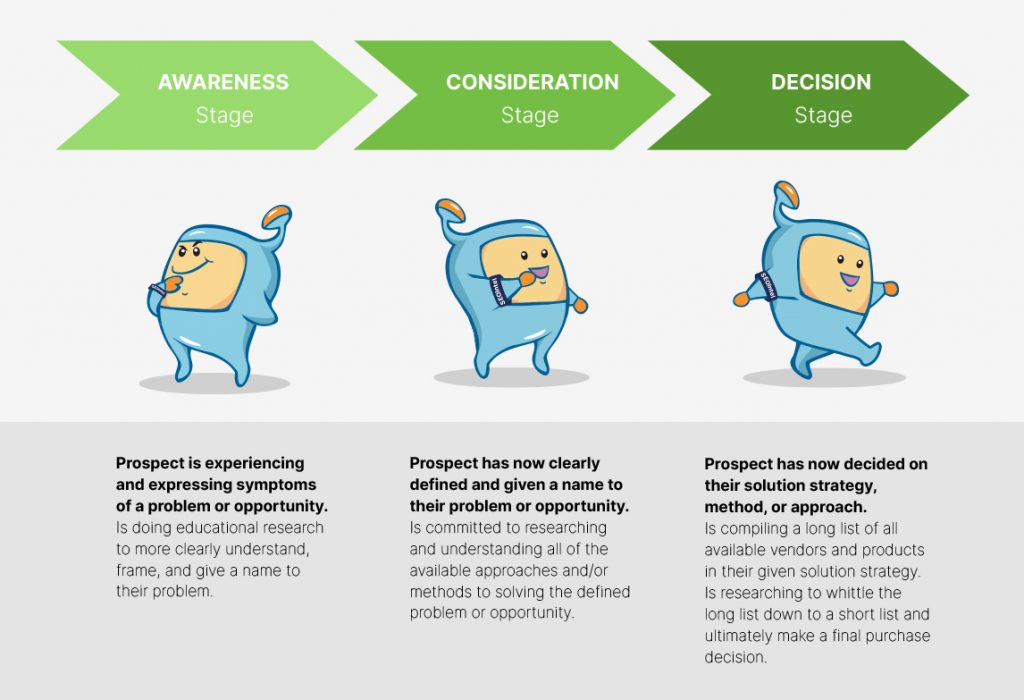
The following can be your action plan for the content production stage:
You might have already heard of this free tool to get a list of keywords that you can use for your content multiple times, but this is gold!
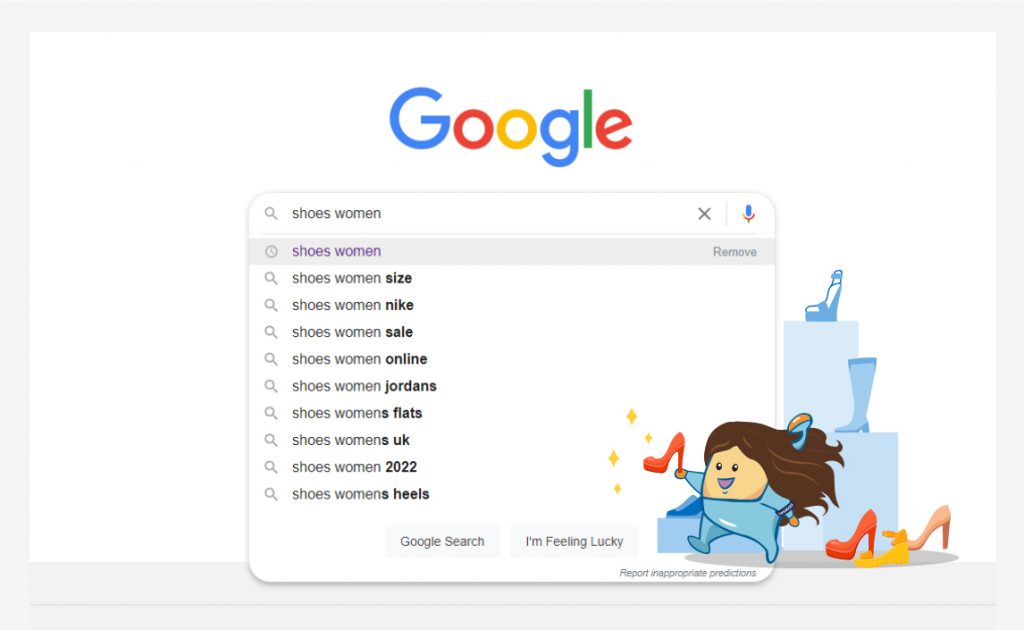
To begin, consider the keywords you wish to rank for on Google. Let’s say you own a shoes shop, obviously you would want to rank your content for commercial keywords like “shoes shop” or “shoes store”, but don’t forget informational keywords like “tips on buying shoes” or “how to spot fake shoes”.
Remember to include long-tail keywords in your list. These are frequently well-thought-out inquiries expressed as questions or sentences.
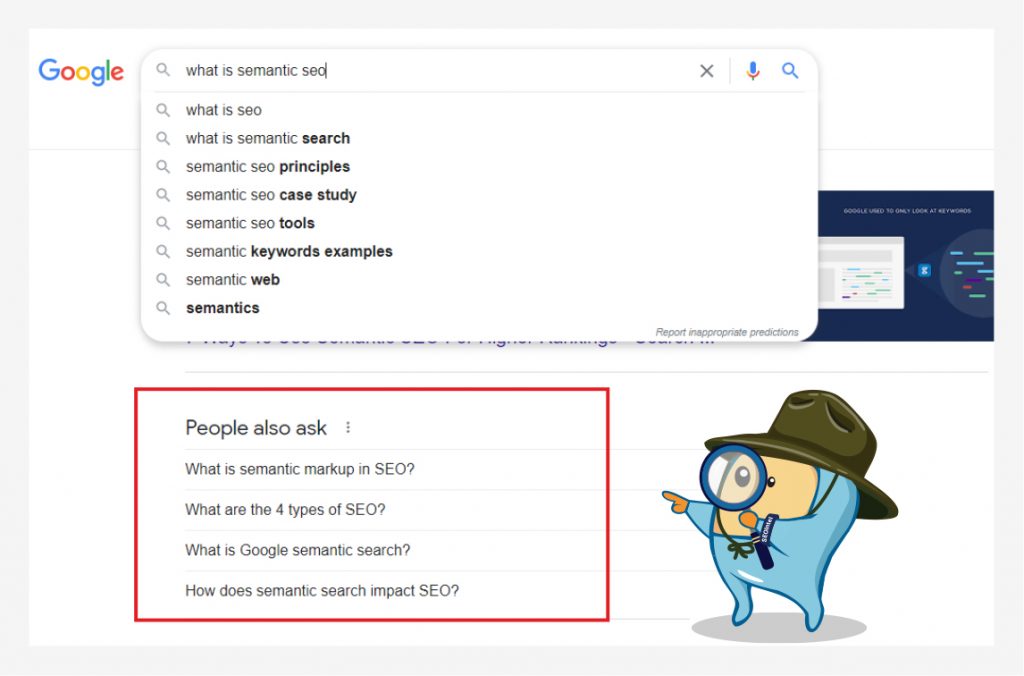
Consult the “People also ask” area and type those inquiries into Google to see what autocomplete results you’ll get.
Alternatively, browse to the bottom of Google page one results to get a list of related search queries that can help you come up with long-tail keyword suggestions.
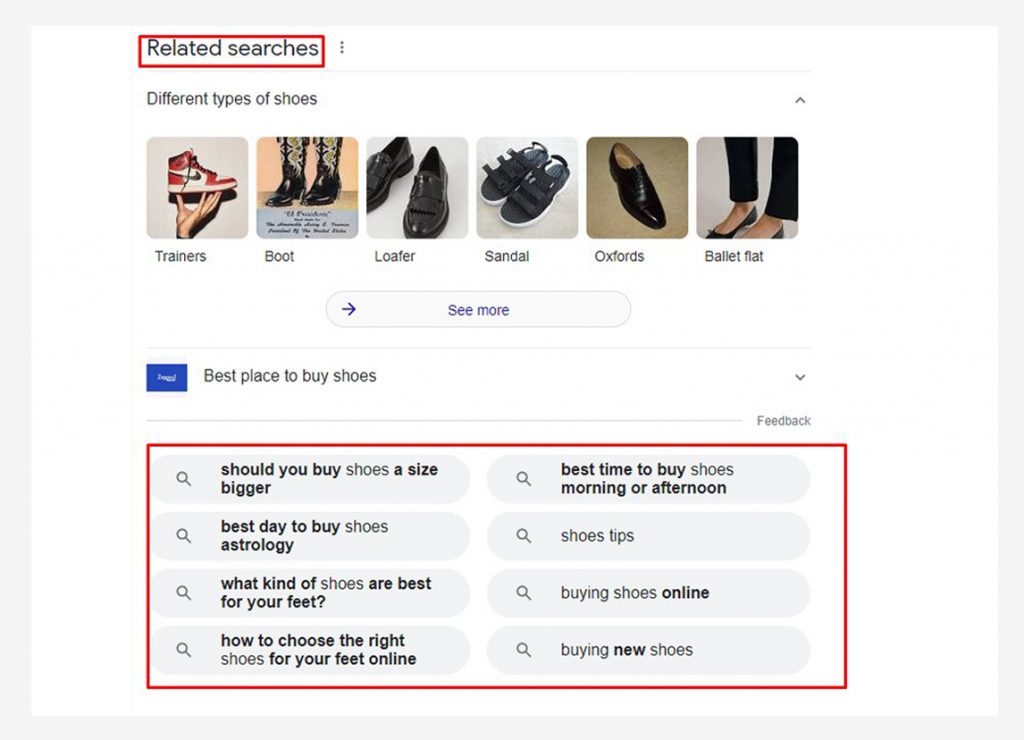
Synonyms and LSI keywords can also be found using Google Search. Although they are sometimes misunderstood, not all related search phrases are synonyms.
With the autocomplete option or the related searches at the bottom of the SERP, you can locate some synonyms and LSI terms.
You can go on and on this way to gather all the queries Google has to offer. And maybe looking at these keywords will help you come up with some more ideas or related queries of your own.
While using Google is an old-school way of collecting semantic data, you can also speed things up and get better results with specialized semantic SEO software.
The Keyword Suggestion Tool from SE Ranking has a massive database that goes beyond search engine suggestions. It has over 2 billion distinct search queries, allowing you to create thousands of keyword ideas in just one click.
You can see a variety of information for each phrase, including the term’s Google search volume—the number of monthly searches the keyword receives. Shoes store, for example, receive 40.5k monthly searches.
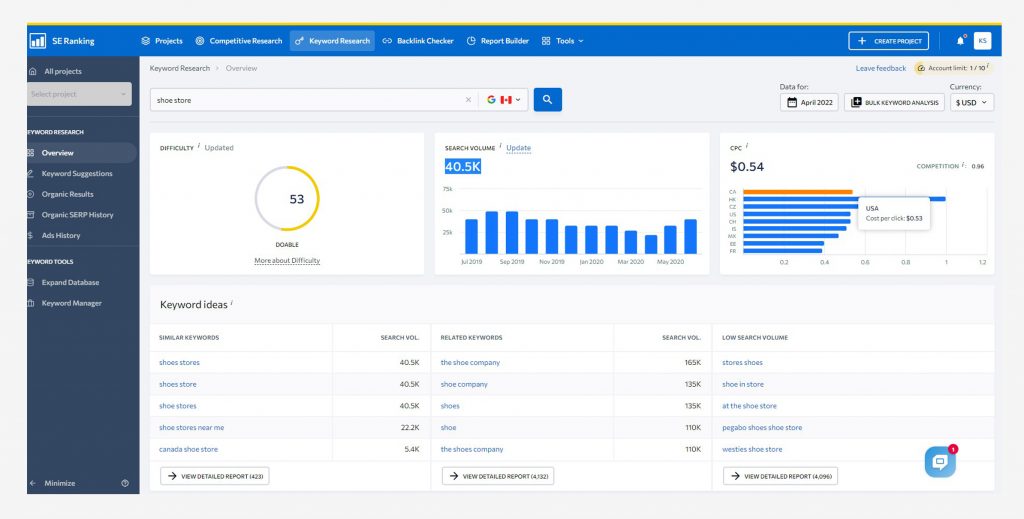
You can use filters to exclude keywords that you don’t want to deal with. You can, for example, filter out keywords with a very high search volume, which are usually too broad and competitive.
Check out the Related and Long-tail Keywords pages for even more ideas. Unlike the Similar keywords tab which only shows search terms that contain your seed keyword, the Related keywords tab shows all types of semantically related searches.
Finally, SE Ranking makes it simple to get keyword suggestions from your competition. You don’t even have to choose which competitor to investigate—the Competitor Research tool will discover your top SEO competitors and generate a list of keywords that they rank for. You’ll be able to uncover some less-obvious terms relevant to your business specialty this way.
After you’ve gathered keywords from all possible sources and organized them in a spreadsheet, you’ll need to delete any duplicates before moving on to keyword clustering.
Examine your list and consider how you may organize terms into different categories.
To score well, your content must fulfill readers’ intent, not just stuffed up with the keywords. The trick is to consider the topic rather than the keywords, group the topics together, then generate an exhausting content that tackles all related topics. It’s up to you to interpret these keywords correctly in order to best meet the needs of your clients.
The next stage is to fine-tune your SEO semantic writing by using structured data, internal linking, anchor text, and other techniques to optimize the content.
Use structured data—a format for classifying the content on a page—to help Google understand your content better. Structured data is a language that tells search engines how to present content in an appealing way.
Check Nike’s website.
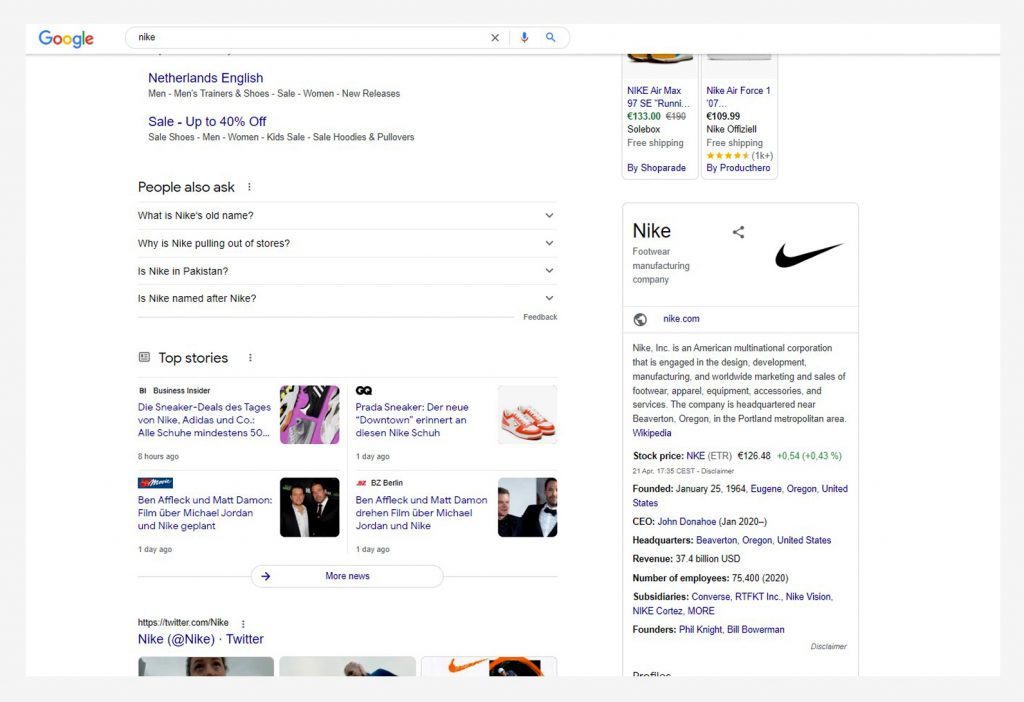
Google’s Knowledge Graph provides broad information about their company, such as when it was created, who the founder is, the customer care hotline, subsidiaries, and so on.
Users can view the most recent news immediately in the search results since the structured data identifies certain aspects of the target keyword or query.
For more details on Schema or Structured Data, checked out Clint’s Schema course in SEOIntel.com
Your content will appear in the proper spot in search if you have a well-thought-out internal link structure.
Three elements make up the internal linking structure:
By connecting pages together, not only can you make it easier for people to traverse your site, but you also make it easier for Google to crawl through your site and find new pages. For the query “sneakers for kids,” a company selling sneakers, for example, can have a general “sneakers” page that displays higher in the search results than a “kids sneakers” page. This appears to be irrational. If the main category, on the other hand, links to the “kids sneakers” page, Google may be able to favor the subcategory page for the given query.
For more information on internal linking, check out our Internal Linking Guide.
Make sure your page has topical anchor texts when setting up internal linking.
An anchor text appears in the HTML code of a page as follows:
<a href=”https://www.example.com”>Anchor Text</a>
Let’s say your page has a lot of bike-related anchor text, then Google will use it to determine whether your content is relevant. There are a few things to keep in mind whether you’re using external or internal anchor text:
Use natural anchor text to present users with relevant benefits.
To keep things natural, use long-tail keywords.
Combine several anchor text types, such as branded anchor text and link lists.
It’s all about relevancy and value when it comes to creating content and optimizing it for search. Even if your page has a high authority, if the content isn’t relevant to your topic, it won’t rank. According to the fundamentals of semantic SEO, you must adapt your sites for natural language search, answer as many queries as possible, and optimize your content so that Google can interpret it correctly.