Are you pondering, “Why has my site traffic dropped?”. Drops in traffic is very stressful for site owners and if you are one of them who suddenly experience a drop in traffic, this is a big problem for businesses. Traffic drops can cause sales losses, especially for e commerce sites and businesses. If you are wondering and have questions, here are 5 big reasons why your site’s traffic may be dropping
While you read this, I want you to keep one question in mind:
At the Time We Began Seeing a Decline, Did We Make Any Changes to Our Site or our Marketing?
Seeing (or being convinced that) the number of visitors to your website is declining can be quite discouraging. What can make it worse is not knowing why the drop is happening. Having some idea as to the potential reasons why a website’s traffic may be dropping is key to rectifying any issues that may have cause this traffic drop.
The Big Takeaway: Identifying the Source of Traffic Loss
There may not be one single source of your web traffic loss–it could be due to a number of reasons. Let us delve further into the different causes why your site’s traffic has dropped and particular ways that can be done to solve it and get your site’s traffic back up again.

Although the reasons why your website may be losing traffic can be more specific than these, here are the 5 big reasons, or categories, that they fit into:
These are issues having to do with either your server, host, or perhaps some code on your website that is causing issue on your site. Technical issues include a slow loading website, some pages on your website that are showing 404 errors, crawl issues, and the like. These type of issues may cause a loss of visitors and an increase in bounce rate when visitors check out your site. It is possible that when your website loads slowly, people who visit your site just changes their mind and leaves your site.
While technical issues are usually unseen by your visitors, on-page issues may be factors that are visible to humans. That’s not to say that all on-page issues aren’t also technical– again, there may be overlap. However, on-page issues may be ones that you can (hopefully) more easily see. On-page issues can include content that is low quality. Content that does not satisfy the intent of the user can cause the user to leave your page, thus your site getting high bounce rate sessions, and which can cause a drop in rankings and drop in traffic to your site. Content quality is also a factor that needs to be checked if it can indeed be the reason for your site’s traffic dip.
These are possible issues that occur off your website (and are usually outside your direct control). Examples of this is when your site has un-natural links going to your website which Google discovers and has caused a drop in your rankings, which then causes a drop in organic traffic to your site.
While these can also be thought of as off-page issues, I wanted to put them in a separate category because they may be easily overlooked. It could be that your marketing and advertising campaigns aren’t working anymore. The hype has died down. People are tired of seeing similar ads and marketing materials from you, so they do not get interested in visiting your site anymore. A way to check your marketing and advertising campaigns is by using Google Analytics. Maybe it is also time to refresh and redo your Ad and Marketing campaigns and doing so may help increase your website traffic again.
These are factors that can affect things like your website’s position on the search engine results page for a given keyword phrase. If your site experiences drops in rankings, it can also be expected that you would experience a drop in organic search traffic going to your website. Their are various tools that you could use to help you track rankings of your websites and see if the dip in traffic could have been caused by a drop in search engine rankings.
While some potential causes may fall into more than one category, I feel that these five cover a wide enough scope that most possible causes of low website traffic can be discovered here.
Are There Pages on Your Website That Are Not Mobile-Friendly?
In the SEO field, we’ve noticed that a healthy portion of searches are done on mobile devices. This has been a growing trend for years and more and more people are conducting searches on their mobile devices rather than on their computers. Due to this, it is best to make sure that your website is mobile-friendly and that there is no reason for users who visit your site to suddenly leave your page when they see that your site is not optimized for mobile.
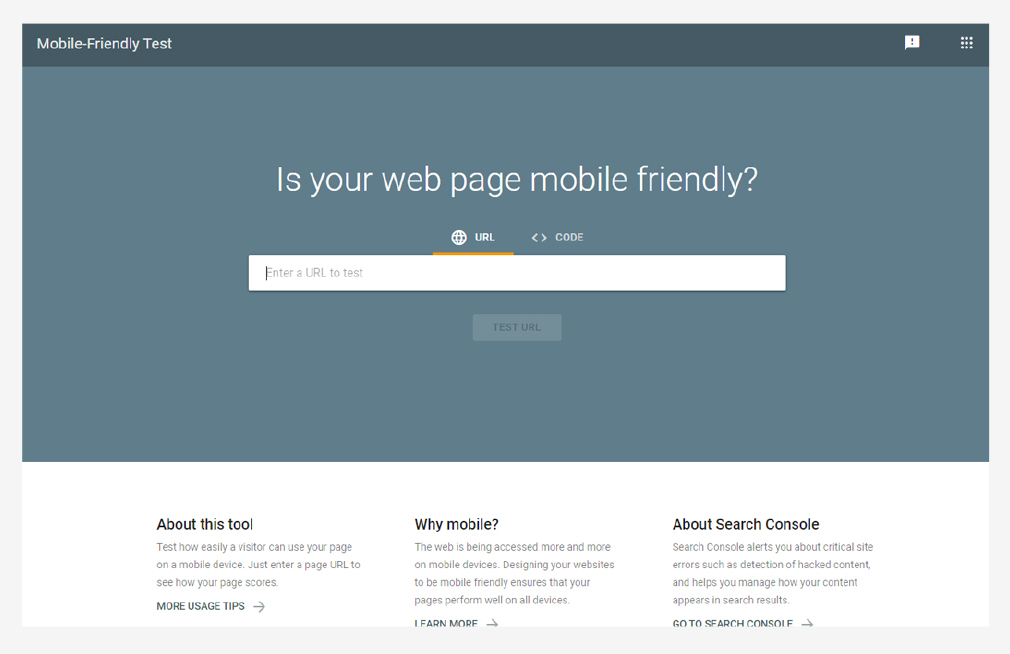
You can use Google’s mobile-friendly test tool to see if a certain page is mobile-friendly: https://search.google.com/test/mobile-friendly
A redirect is simply a technical way of directing traffic from one url (or page) to another.
They’re almost like road detours. If content on a certain page isn’t available (for example, a product isn’t in stock), then a redirect can send traffic to another page featuring a similar product.
If a redirect is removed or changed, it could take Google a while to re-evaluate the content on the target page and re-rank your website.
Another factor is if your redirect is not set-up properly, which could be causing errors on your site.
There are different tools that you could use to make sure that your redirects are working as they are supposed to. Simply let the tool crawl your site and it will check if the redirects are working fine and are not encountering any problem.

This one’s simple: if there’s an error on your robots.txt file that instructs search engine crawlers to NOT crawl your website (or a certain section of your site), then your website (or a certain section of it) may not be indexed. Another is that, your site may also have crawl errors that are making search engine robots unable to crawl your site. Checking search console and other seo tools can help determine if there are crawl errors being encountered on your site.
Hence, it probably wouldn’t show up on search engines results pages.
Sometimes, for various reasons, webmasters may move their content from one URL to another.
One method of ensuring that visitors who go to the old url are sent to the new, intended one is via use of 310 redirect.
However, if you do 301 redirects a lot, it may be difficult to keep track of all of them and sometimes, a mistake or mistakes can happen. And then, if one of them is missing or isn’t updated, and the search spider finds it and doesn’t know what to do with it, you could lose rankings and visitors, particularly if that older page was ranking.
A broken redirect is simply a redirect that, for whatever reason, doesn’t work. Again, if a search engine bot comes across something like this, it may drop that page from the search index.
There are a few types of security issues that can beset a website.
A rare one is if a hacker gets into your website and installs malware on it. Then, if a visitor comes, they won’t see your website, and if you use an analytics program such as Google Analytics, that visitor may not be counted on your site, which might be why you see a drop in site traffic.
Content is one of the most important part of websites. A site with low quality content will meant that users will not be happy with your website. They will end up leaving your site and not returning again. Low quality content also means that Google will not rank you. When publishing content, make sure that the content is valuable to both users and search engines.
If you also rely on organic search traffic for your website traffic, it’s possible that a competitor has put out higher-quality content that excels against your content that used to get traffic? It is good practice to update your site’s content from time to time and make sure that your content is high-quality and that you have good landing pages.
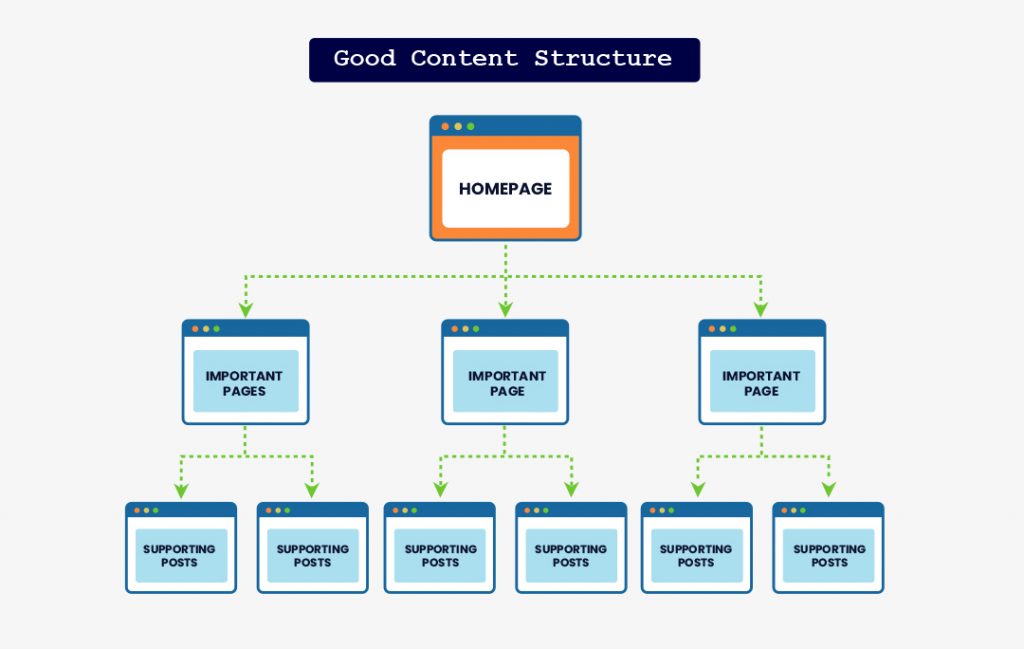
This one’s a little less obvious, but it actually goes hand-in-hand with quality content.
High-quality content usually has a good flow, and good flow comes from good structure. People are not exactly reading the content of your site. Most just scan through to search for the answers to their questions. Since people are in a hurry and would just like to read content releacant to them, it is important to have good content structure.
Good content structure means that you make use of the htags well, highlighting topics of importance. Keep paragraphs short and simple to read through, and make use of bullets whenever possible. Too long sentences and paragraphs not formatted well can cause users to find your content tedious and they end up leaving your page and going to another site. Thus, causing an increase in bounce rate, benefitting your competitor more, and causing drops and rankings to your site.

If you have a good tracking system or tool, you might be able to actually see the data for traffic sources that are referring traffic to you. There are also tools that are diagnosing traffic and can see which traffic source has been affected and has caused the change.
If you track your search rankings, then generally speaking, where do your pages rank now compared to last month (or before you noticed a sudden drop in traffic)? Did you also experience a drop in rankings? Is there an algorithm update that could have rolled out that might have also caused a sudden drop in rank and therefore, a traffic drop to your website?
I know what you’re thinking: “How is it possible to track the wrong rankings?”
Well, it can happen if you have several variations of a page that offer the same product (or variations of a product).
If a different page is ranking than the one you’re tracking, that might explain why you’re tracking the wrong rankings (page, in this case). Maybe it is also best to do keyword research for your page to see what particular keyword can be more effective for your site. Also, it is best to target one keyword per page as multiple pages targeting just one keyword is bad seo practice and a disservice to your pages.
While the term organic traffic is usually used in terms of search engine traffic, here I’m considering all traffic sources that you don’t pay for.
This includes your company’s YouTube videos and social media posts.
If you rely on organic traffic, is it possible that there has been a dip in traffic any of these other sources? Perhaps it’s time to release new videos and publish more content, make your youtube channel and social media more active, in order to have more people visiting your web page again. These changes can be a way to restore traffic to your site. There are various youtube tools and social media tools that can help you monitor data in these channels.
It’s been said that if a site is found to have done something that’s against the spirit of Google’s Webmaster guidelines, that site may be penalized.
A penalization can result in a reduction in rankings, which means a decrease in traffic to your site.

While most Google penalties may be algorithmic, a manual action penalty occurs when a human reviewer at Google actually comes to a page, assesses it, and determines that that page isn’t compliant with Google’s webmaster guidelines.
If you feel that this is the case, then please have a look at Google’s webmaster guidelines and determine how you can better comply with those. Looking through Google Search Console’s Security & Manual Actions menu for your site will also show if you indeed have a manual action penalty for your site.
Although Google constantly does refinements and minor changes to their search engine algorithm, there are a few milestone changes that are significant enough that they’re named.
With a search algorithm update, you can lose traffic because if other sites (like your competitors’ sites) are determined to be more in line with the algorithmic change, then their position in the search results might rise, while yours lowers.
Well, it may take a bit of investigating to determine if a site was actually penalized, here are a few first steps that come to mind:
1. Enter your robots.txt file into Google’s robots.txt Tester, checking to be sure that Googlebot isn’t being blocked.
2. Ensure that your site is up and well and there are no indexing issues encountered.
3. Use the site: search operator to see if your site is indexed in Google. So, if I wanted to see if seointel.com is indexed, I’d go to Google and enter this:
Site:seointel.com
4. If Google shows no results, then you have a big clue. If you see no results (and you entered your site correctly), then it means that your site isn’t indexed (or if it was, it’s been de-indexed). If your site is in Google’s Search Console, see if there’s an explanation as to why it’s not indexed.
5. If Google does show results, take a look and see which pages are listed first.
(Though I’m not sure if this is confirmed, I heard that the home page should be listed first, and that there’s a sort-of descending order that pages are listed in, so that the pages that Google thinks are most important show up first.)
Link Spam Will Cause Google Traffic Drops
Link building is a very nuanced issue, but let me put it this way: it’s fine if a site gains inbound links naturally.
However, link building for the sake of link building is frowned upon, and link building done to excess (a mass number of low-quality links) can cause a site to lose rankings, and hence, lead to a traffic drop.
A way to look at your website links is to use a link analysis tool, in order to check what kinds of links your site has and if spammy links are indeed the cause for your traffic drop from search engine traffic.
This has to do with local, brick-and-mortar business marketing.
Basically, a geolocation discrepancy occurs when an address that a visitor sees is not necessarily the current location of a business. Or, it could happen when an advertiser or marketer targets an ad to a zip code, but a publisher targets that same ad to an area code.
Let’s suppose that last month, your site was in the #1 position on the search results page for a given search query (or keyword).
And let’s suppose that a few of your competitors improved their search engine rankings (via better content, updated content, a better click-through rate, or any number of improvements).
This month, due to their improvements, your competitors out-rank you. Your site is now in position #3 or worse. This would account for a change in organic traffic levels.
For example, if 100 searchers see a results page, and one of those results is your site, and 3% of those searchers click on your site, then you have a 3% CTR.
It’s theorized that your CTR affects your search ranking.
So, let’s say that next month, another 100 searchers see a results page, but this time, only 2% of them click to your site, then your CTR will have dropped by 1%.
This, in and of itself, can account for decline in traffic. (Actually, in this example, the 1% drop in CTR actually results in a 33% drop in visits!)
So how do you fix this? Check the title of your page and the description and update it to make it more interesting for users and increase the chances of them clicking on your search listing. On a seo perspective, make sure that your title and description includes your keyword. Optimize your page titles and descriptions for both search engine by using your keyword and for your users by making them interesting enough to warrant a click.
If there’s something wrong with your tracking, then the numbers and data it displays may be erroneous, and you might see a supposed drop in traffic whereas, in reality, nothing big has changed.
You can always look at your site’s revenue to see if it confirms a drop in traffic.

If you’ve redesigned your site, particularly structurally, and you’ve moved around some pages, then your rankings (and traffic) may drop as Google re-evaluates your site’s new structure. Recheck your site and make sure there are no broken links or technical seo issues that could be causing the drops in traffic. Check Google Search Console for any problem on your web page that may need to be fixed. Check your site’s urls to make sure they are set correctly and that there are no pages that are no-index. No-index often happens when redesigning a site and it could be that your designer might have missed removing the no-index code.
Google has it’s very own tools that you can use to check for any issues that your site may have. These are the Google Search Console and Google Analytics.
In Google Analytics, here’s what you can do:
1. Look at your stats from well before your traffic started dropping.
2. Then, try to determine the week or two before it started to decline.
3. Does that date correlate with anything internal or external? Did your team do any major site overhauls? Was there a Google search update? Did you stop (or start) a new marketing campaign?
These are questions you can use to begin finding out why your site’s traffic dropped. Always try to check and monitor Google Analytics in order to have traffic data points for your site. It is a very helpful tool for tracking and diagnosing traffic.
This one’s straight from one of the help pages in Google Search Console. Basically, if your site is an https, but in Google Search Console, you declare that it’s an http (without the s), then you may be “missing” some traffic stats because the traffic going to the https version isn’t being counted. Check your urls and make sure they match.
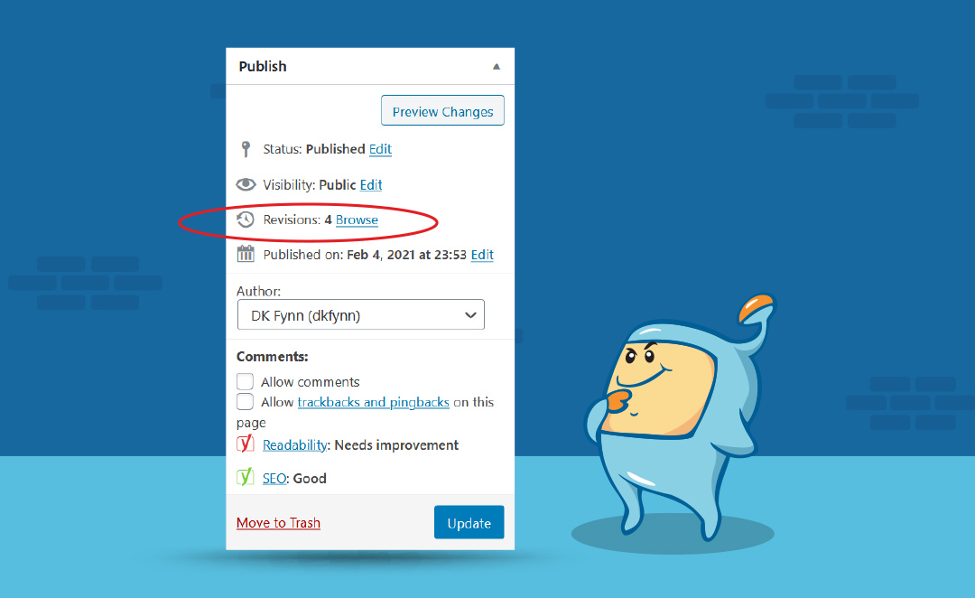
In some website platforms (I’m most familiar with WordPress), you can check the revision history of individual posts. What you can do is, if you find that traffic to a given page has been declining you can check the revision history of a given post.
If the date of your last change matches up with a change you made to that post or website, then that may explain why you’re seeing fewer visitors.
An annotation in Google Analytics is basically just marking a date on a calendar.
For example, let’s say that next week–Wednesday, to be specific–will be the last day of a certain ad campaign.
Ideally, you’d annotate (or mark) that date in Google Analytics.
A few weeks (or months) down the road, if you notice anything drastic, you’ll be able to go to Google Analytics, look at the date you annotated, and perhaps gain some insight and see if the traffic drop may have been caused by some of your marketing and ad campaigns.

I feel that if you’re in a market that’s seasonal (winter tire installation, camping, graduation gowns, holiday gifts, etc.), then of course, your website traffic may ebb and flow with the seasons and different period of time and lesser people visiting your site since it is not the season for it.

Basically, content pruning is ‘trimming the fat.’
For example, let’s say that a website has some pages that are just low-quality filler pages that don’t really do anything for anyone, and don’t get a lot of traffic.
Content pruning would mean deleting these pages and blog post– even if they’re indexed by Google.
Of course, webmasters won’t like to do this. But doing this ensures valuable traffic to your website.
How do you still have everything indexed without pruning your content?
By using a canonical tag, you don’t have to prune or delete content, and you’re referring to the good page that you actually want traffic to go to. Canonicalization can have some good SEO benefits.
I hope this article has given you a lot of insight into the possible causes of why your website’s traffic has dropped, and hopefully, you now have some idea of what to do next and would be able to set up a contingency plan when a traffic drop happens again on your websites.
Is your organic traffic still low and not sure what to do? People are still not visiting your website and not sure what the problem is? Need help in boosting your search traffic? Maybe you need quality links to help you boost your site and rankings, and move you up further in the search engine search results page? Check out SEONitro 3.0 for your link building needs and if you are not much into links and need proven and tested seo data on what ranks and what doesn’t, check out tests we’ve done in the SIA.
Go through our site for more articles and resources that could help with your seo and getting your site ranked, and therefore get increase your website visitors.
