When it comes to Search Engine Optimization, on-page optimization is the easiest as your own site is something that you have control of and can easily make changes in, in order to optimize your page and have a better chance of ranking higher in Google and other search engines. In addition, what makes on page seo important is it is the foundation of optimization as without a properly optimized site, it would be hard to rank a site by just using off page seo. There are a lot of information going around though as to which on page factors work and which factors do not work. Which factors are the most important ones and you should be working on when you set up a page? In the SIA, we tested known on page SEO factors to come up with the list of 5 critical on-page SEO factors that you should work on, in order to increase your search engine rankings and gain organic traffic to your site.
Note: The terms keyword and keyword phrase are used interchangeably. Generally speaking, a keyword is one word, whereas a keyword phrase is 2 or more words. A lot in the SEO industry uses the term keyword as a sort-of catch-all term encompassing all keywords, regardless of whether it’s a one-word keyword or a keyword phrase.
If you’re new to on-page search engine optimization, this is a great place to start. While we won’t exhaustively cover every detail of every single on-page SEO factor, we’re going to reveal the 5 most critical factors for on-page SEO that we’ve proven that would help move a page up, so that you do not waste your time with low-value tactics that do not work.
But before that, let’s start from the beginning.

Search engine optimization is incredibly dynamic: the search algorithms of Google, Bing, YouTube, Amazon, and most advanced search engines take many variables into consideration when it comes to search rankings and ranking relevant content.
Quite simply, one can say that SEO consists of what a page says (its content), combined (possibly) with what other pages say about that page. In other words, on page SEO refers to the content of a page, and off page seo is the reputation of a page. (That’s a bit of an oversimplification, but it drives the point.)
Broadly speaking, one way to categorize the various aspects (or factors) of the search engine optimization of a web page is to say that there are on-page (and on-site) factors, and off-page factors.
As we know, Google ranks web pages (not just websites, but individual web pages, which is why a certain page of a given site may be more optimized for a certain query, or keyword, than another page on the same site).
The question here is: When you see a search results page, why do you see certain pages (aside from any off-page factors)?
That’s likely because of the on-page SEO of those pages: the content on the pages you see are what Google thinks mostly resembles your query.
So, it stands to reason that, all other things being equal, the page(s) with the best on-page SEO stand a better chance at being discovered for a given search term which is why optimizing web pages is important.
That said, you probably know (or sadly, will soon find out) that there are many myths, uncertainties, and downright lies in the SEO industry. So much so that even known reputable sites also release information that are not really true and have not been tested, furthering the misinformation.
And this, I should say, is not necessarily due to any malicious intent: search engine algorithms are trade secrets, so the best we (the SEO industry) can do is make educated guesses and statistical correlations to try to identify the factors that we think make the biggest SEO difference.
This is where we, the SEO Intelligence Agency, come in. The aim of the SIA is to try to bring you research-proven discoveries. In an attempt to meet our aim, we’ve conducted several SEO experiments to try to identify the verifiable facts vs the unknown uncertainties.
Around 2016, we conducted a test to try to determine which on-page SEO factors are the ones that make the biggest difference and can boost rankings in search.
Before I list these, I’d like to say that just because our test result found that there were 5 which were critical, none of the other 7 on-page factors (or, perhaps any of the more subtle on-page factors) are without value.
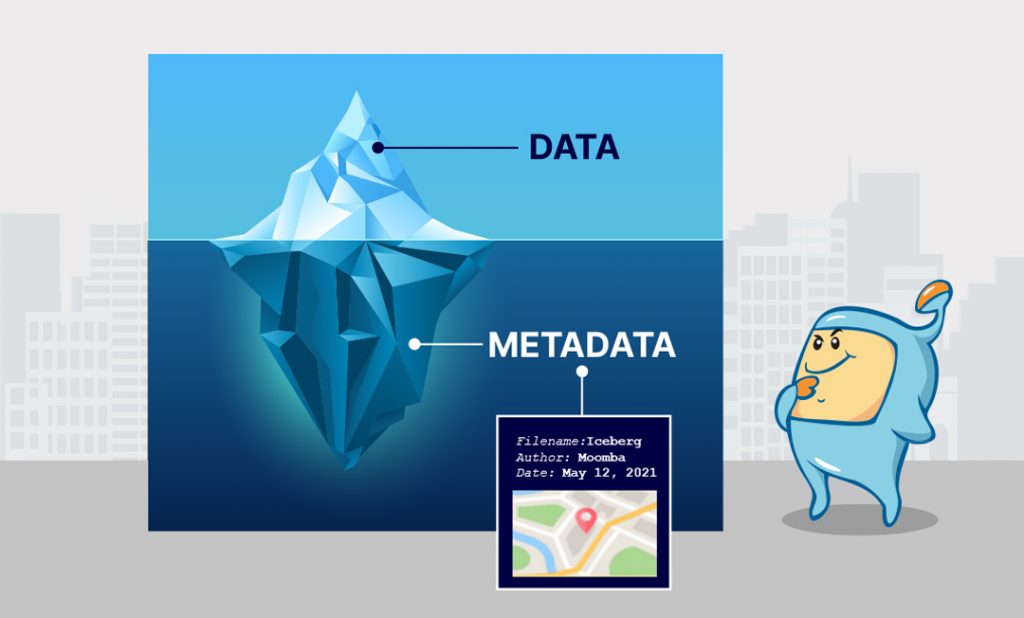
As a side note: the prefix meta- (or meta without the hyphen), just means metadata. Metadata is just data (words, in our case) that might not be on the actual displayed page itself, but is nonetheless part of the file or overall data for that page.
That is, it’s usually data that human users may (or may not) see, but that search engine crawlers can usually see. Metadata is useful for classification, categorization, and identification.
The keyword phrase for this article I’m writing is on-page SEO. If you look at the full URL (the web address) of this page on a desktop or laptop browser’s address bar, (assuming you’re seeing it on SEOIntel.com), it’ll very likely contain on-page-seo.
If the page you’re on has a proper title tag, if you look at the text in the tab, what you’re seeing is likely at least a portion of the text in your title tag. It’s basically a document title, similar to the title of a .pdf or a Word document (not to be confused with a file name).
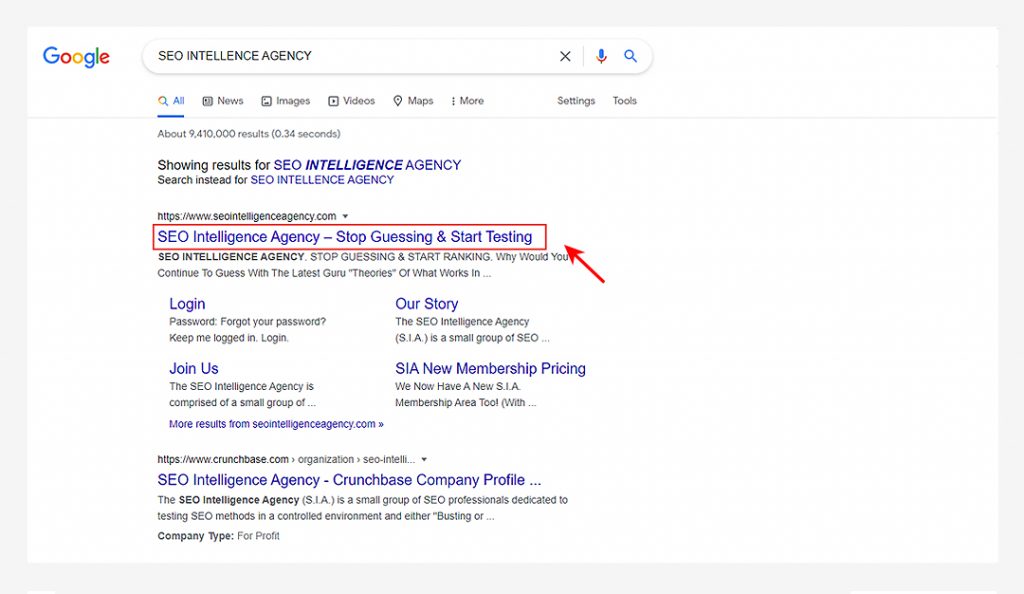
When you look at a Google search engine results page, the blue text that you see is basically the title tag text of that page (or, at least the portion of it that Google thinks is relevant to your search query).
You want to have your keyword in the title of the page you want to rank (and preferably at the beginning of the title tags).
If you have a good content management system (or site-building platform), such as WordPress, Wix, Shopify, and a host of others, the title tag is usually the equivalent of the title of your post, product, or blog entry.
Because it’s said that the search results will show up to 60 characters of a title text, try to keep yours up to 60 characters max (and preferably, quite a bit less, as you have to consider mobile search or search that is done in a mobile device).
A meta description is basically a description of an individual page. It can be read by search engine bots, but not always by humans (although it can be displayed on search results, and it’s recommended that you have this text in the actual content that people will read).
Try to keep your meta description to well under 120 characters, less for mobile users.
It’s been known for years that Google doesn’t really consider the meta keywords tag as much of a ranking factor.
That said, it may be beneficial to use this tag if you want other search engines to know what your page is about.
To be honest, this is one factor that you probably don’t need to worry about.
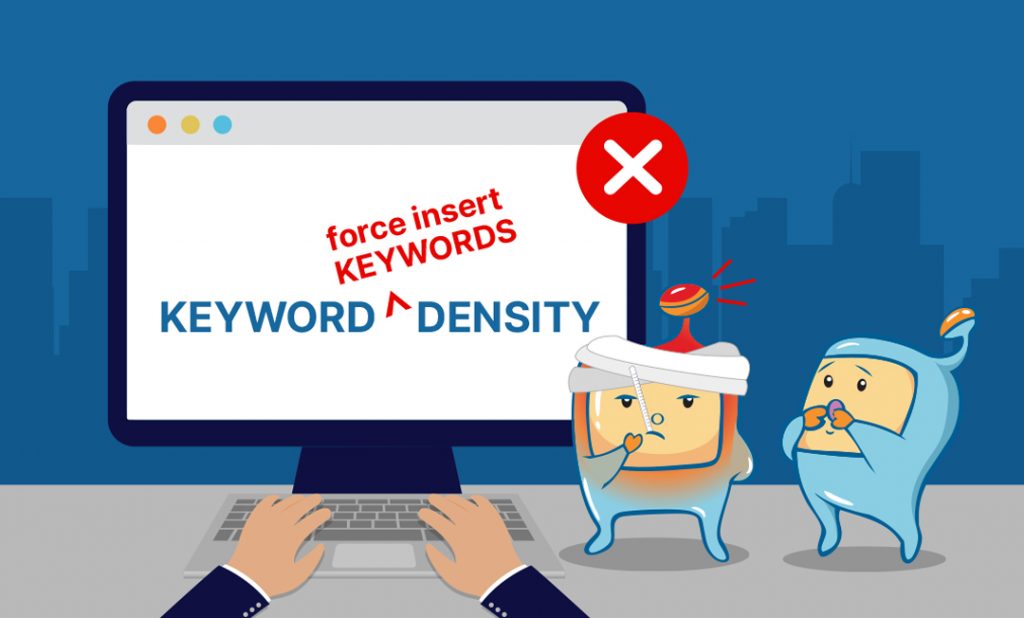
Keyword density, basically, is how much the percentage of a given amount of text (in this case, the content on a page) is the keyword in question.
Someone who was giving advice on keyword density might say, “You want X% of your word count to be your primary keyword.”
The problem with keyword density is that some people take it too far, and it causes them to try to force the insertion of a certain keyword phrase (especially if that phrase is 3 words long) into an article, which results in ungrammatical inconsistencies and unnatural-sounding reading. Others also end up keyword stuffing or using too much of their keywords on their content, which can also end up being of detriment and over-optimizing a page.
It also doesn’t take into account related terms that would naturally occur in any discussion on the given topic.
“Write naturally,” is the wise advice that’s given.
Have your keyword phrase in prominent areas (which we’ll show you below), and you’ll do fine.

There are 6 types of Headline tags or htags, ranging from H1 to H6, in descending order.
If you were writing a paper, perhaps H1 would be your title, H2 would be second-level titles (or sub-titles), H3 would be your sub-sub-titles, and so on.
Likewise for H tags, and the most important one to have your keyword in is the H1 tag.
If you use a good site builder like WordPress, this is very likely taken care of for you: just enter your post’s title, and a good WordPress theme will make sure that that title is also in the H1 of that page.
Not as prominent as H1, it’s still good to have your keyword here.
Though not as a determining factor as H2, it’s still good to have your keyword (or other relevant keywords or keyword variations) here.
Although H4 is certainly not used very often, you can have sub-topic keywords or long-tail keywords in your H4 tag.
The keyword of this article is on-page SEO.
On-page SEO, again the keyword phrase of this article, deserves to be italicized.
What does a blind (or vision-impaired) person do if they come across an image they see on a web page?
Well, if they’re using a screen reader software, the screen reader may pick up what the image is about, and, in its computerized voice, tell the person what it thinks the image is about.
This may only occur if there’s an image alt text used. Image alt is simply text that may accompany an image so that a screen reader can pick up on it.
That’s why, aside from any SEO benefit, it’s good to use an image alt for your images, especially if you’d like to make your site more accessible to comply with the Americans With Disabilities Act.
Using your keywords in the image alt tag also helps the image show up in Google image search.
Go ahead and use each of these 12 (as well as the other tips we’ll reveal later below), but try not to be too fanatical about them. Just write naturally and create natural-sounding content without trying to artificially insert keywords somewhere just to up your keyword usage.
That way, you’ll reduce the likelihood of over-optimization.

These 5 are:
(I put meta in brackets because the title tag isn’t really a meta tag, though some imply that it is.)
Anyway, having your keyword in the portion of your page code is a key factor. Being that it’s essentially the title of the document, it’s easy to understand why this is critical. Both search engine crawlers and human visitors rely on the title of the page to know what the page is about and decide if the page is relevant to their search. Thus, the number one factor.
Well…I don’t think I need to explain this one.
What I will say is to write high-quality content that is natural and use other terms that are in common usage when your keyword is the topic of discussion.
This is advised not just for written content, but also for image optimization (name the image file after the keyword or subject of the image). Have a seo-friendly url that makes use of your keyword as having your keyword in your url also helps search engine robots determine what your content is about.
This makes sense: the <h1></h1> is the most heavily-weighted of the H tags and same as with the others, is another area where search crawlers determine what the topic of the page is.
Even though a keyword in bold in a ranking factor, try not to bold every instance of your keyword, as it may look odd. Once or twice is probably fine.
Having your keyword in these 5 critical on page factors shows that your page has relevance for a search query using the keyword. Make sure to incorporate all of these on your page. In the following section, I will be talking about additional tips on optimizing your page for search.
By taking the advice of everything I have to say here, you’ll have taken many steps toward optimizing your content for SEO.

This one makes sense, both from a reader’s and a bot’s perspective. If you’re searching for information, as soon as you land on a page, and before moving on, you want to be sure that the page contains the information you’re looking for.
From a bot perspective, seeing the keyword phrase (and associated terms) within the first hundred words (and I’d say much earlier than that) is a good way to ensure that the page is about that keyword. When I write, I try to include my keyword phrase within the first 120 characters–not just words, but within the first 120 characters.
Link out to pages on other sites that talk about the same topic yours is on–particularly high-quality sites. This is good for the user, and it seems to show an association with those other sites.
This doesn’t just mean having your keyword in the title, but perhaps first in the title (as opposed to somewhere in the middle, or at the end). The same may be true of your meta description.
This is just a continuation of the point above, with the added advice that, if for grammatical purposes, you have to have your keyword in the middle of the title (or description), that’s fine, too.
Don’t make the mistake that some webmasters do: sacrificing grammar just to fit a keyword somewhere.
Let’s suppose that the keyword that you want to optimize for is how to write an essay.
Well, of course, some people are more specific and may add additional words toward the end of that query, such as introduction, outline, proposal, conclusion, etc.
Well, if you’d like to broadly cover the subject of essay-writing, you can create separate (but of course, related) pieces of content, each on a slightly different aspect of essay-writing. One article can be an introduction to the topic, one can be on writing the introduction of an essay, another can be about outlining, and so on.
And for each of these, in their titles, you distinguish each one by having a slightly different title, such as how to write an essay introduction, how to write an essay outline, how to write an essay proposal, and so on.
Having these modifiers (which is basically making your target keyword more specific), can make your page more appealing to people searching for more specific information.
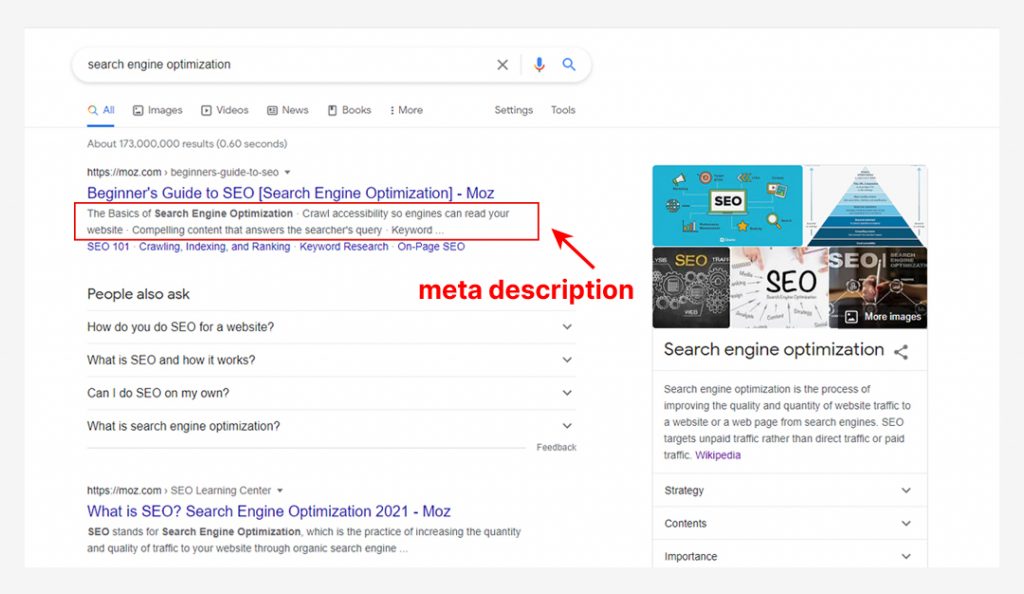
I spoke about the meta description above. Here, I’ll just expand on that: while maintaining grammar and readability, you can try to have as many related terms as you can.
In other words, definitely use your keyword, but do also try to use other related terms.
On a search results page, Google only displays up to 120 characters for your meta description, so keep that in mind.
SEO content is content that you’ve determined has a good chance of ranking.
When such content is professionally created, usually a lot of planning takes place. This includes market research, keyword competition research, copywriting, use of seo tools and content writing tools, content optimization, a professional writer (or content creator), and so on.
Knowing and applying these 5 critical on-page factors, optimizing your page using the other onpage tips I’ve provided, and a high-quality seo optimized content, is a surefire seo tactic that would help you get improvement in your rank.
Want to learn more about SEO and ranking your page on search? Check out our more detailed on page seo guide and how-tos, and our articles on off page optimization and link building. Perhaps you’d also like to learn about other digital marketing topics such as email marketing, social media marketing, conversion marketing, etc.? Check out our site for more articles to help you and your business gain more visibility and brand awareness, get users visiting your page and converting them into customers and sales.
