
According to Google, Page Speed is a critical factor when it comes to ranking sites and how fast your site speed is can affect the rank of your site. But what is page speed? Does it really affect Google search rankings? How do you test page speed? How do you improve it?
In this article, we talk all about page speed – what it is, results of the tests the SIA has done on page speed and if it’s a ranking factor, how to check your page speed in mobile device and desktop device, and tips on how to fix site speed issues and increase speed for both your desktop pages and mobile pages.

Page speed is defined as the loading speed on an individual page on your website. Each page of your website may have different page speeds due to different factors such as the content on the page – images, videos, and scripts added to the page. The speed of a page also relies on the server’s performance, the connection type, and the user’s internet service provider, the user’s device, browser, etc. As you can see, a lot of different factors can impact page speed. Some of which you, as site owner, can control, some of which, you could not. We can only work on factors that we can control such as our website and our server.
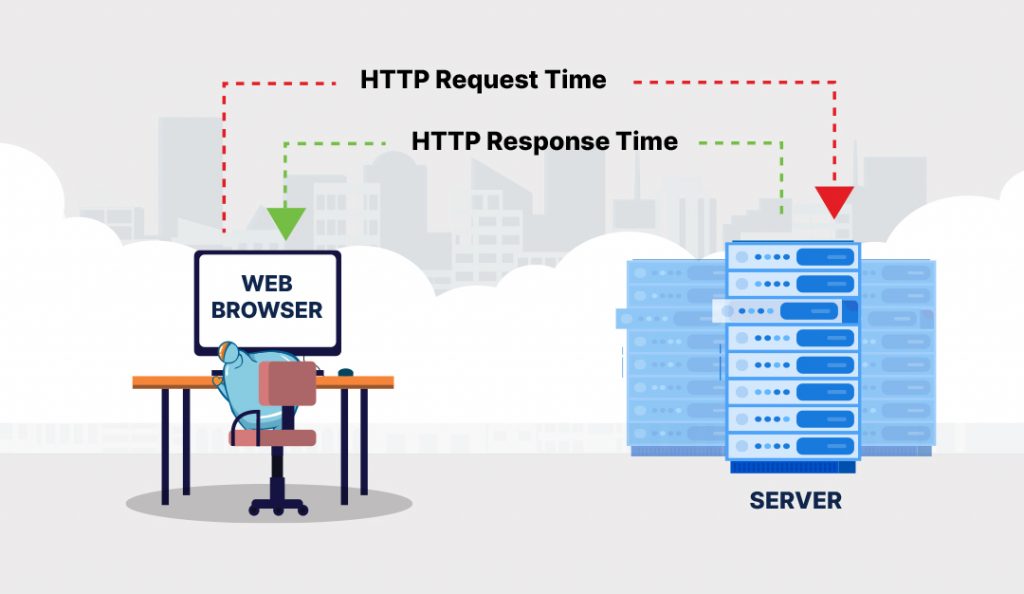
Page speed is measured in seconds and it can be described as either page load time or the time it takes to fully display the content of an entire page or time to first byte or the speed at which the browser receives the first byte of information from the web server and starts loading. Another measurement is the first meaningful paint or first contextual paint, which is how long the site loads enough resources for a user to be able to read content on the page. As you can see, there are different ways of measuring page speed and it is also measured for both desktop and mobile site. This brings us to the conundrum – when Google says page speed is a ranking factor, which is it exactly referring to? Is it the page load time, the time to first byte, the first meaningful paint, or is it all three?

Page Speed is important as Google has directly stated that it is a Google ranking factor and how fast your site is can affect the rank of your site. In addition to this, speed can also affect rankings indirectly as a slow loading site can affect search engine users who visit your site. Users who encounter pages that load slow most often than not, leave the page. This affects your conversion rate and also increases the bounce rate, average session duration, and dwell time of your site, which in turn, can affect the rankings of your site. Google gives a lot of importance to user experience and when it sees users leaving after about 3 seconds, they read this as bad experience to users. Google does not like ranking sites in Google search that has bad user experience.

Google has confirmed that page speed is a ranking factor since 2010 in desktop searches and in 2018, it announced in a blog post that it has also applied it to mobile search results. However, Google is a little vague on what exactly is page speed. I’ve mentioned earlier that there are three measurements to page speed – page load time, time to first byte, and first meaningful paint, and the problem is, Google does not exactly say which it refers to when it says page speed.
In SIA Test 31: Is Page Speed A Ranking Factor, the SIA tested if page load time or the time it takes to fully load a page is a ranking factor. In this test, it was found out that page load time was not a direct ranking factor.
While doing research for the test, Kyle found an article from a Moz contributor who also reached the same conclusion – that page load time is not a ranking factor. What is interesting in the study is that, while page load time is not a ranking factor, the author found out that the time to first byte might be. Due to this, the agency has come up with another test on page speed, this time, focusing on Time to First Byte.
In this test, since it was found out that page load time was not a ranking factor, it was tested if Time To First Byte is what is Google referring to when it says page speed is a ranking factor.
This test checked the rank for pages with a difference of .5 seconds and aimed to understand whether speeding up your site or host will add benefit to your site and help get it ranked higher in Google search. During the initial set up of the test, the team ran into a large issue with Google’s Fetch and Render when TTFB was slowed down dramatically. Google did not even want to process or index test pages with a delay of more than one second, which led them to believe that a high TTFB should be fixed to improve user experience.
Small TTFB adjustment (anything up to 1 second), however, did not add any ranking boost to the pages. However, large adjustments, over 1 second, were a major issue with Google. It was concluded that it is best to keep your TTFB small but not to worry about fidgeting with it too much once you have it under 1 second.
Our tests have shown that it looks like Google refers to Time to First Byte when it says Page Speed is a ranking factor.
Aside from our testing, Neil Patel has also released a correlational study on page speed and in it, it shows a high correlation between sites that are ranking at the top and their time to first byte. It all comes down to user experience, and a fast time to first byte will also mean a faster page loading time, thus, faster page speed, all in all, which means a superior user experience.
This does not mean, however, to only improve upon your time to first byte. While it is important and significant, it’s still important to make improvements wherever possible on the other page speed elements of your site as we are not only making adjustments for the benefit of search engines to get ranked in search results. It is also for the benefit of the user, to avoid bad page experience by having your pages load quickly.
As we all know, SEO is composed of a lot of different factors that work together to get your page ranked to the top. Focusing on just one factor will not get you a higher ranking, however, optimizing each factor, stacking them up together, placing them all in harmony with each other, will get you up there and reaping all those organic traffic from Google search.
Now that you know about the importance of page speed and which page speed factor to give particular attention to, the question is, how do you check your site’s page speed?
When it comes to page speed metrics, there are two types of data that is being recorded – mobile speed score for mobile searches and desktop speed score for desktop users. There are a lot of seo tools out there that can show you the information. Here are just some of them.
Google has its own online tool to check for page speed – Google PageSpeed Insights. PageSpeed Insights scans your page for issues and opportunities that you can do to speed up your page speed. All you have to do is enter your url and it will return results on the performance of your site. It will give you a score ranging from 0 to 100 for both desktop search and mobile devices. This means that you would have a separate mobile speed score and desktop speed score. These scores are based on multiple factors. The higher the score, the better, and a score of 85 and above means that the page is performing well. Below the score will be detailed information on your page speed, issues, and opportunities and steps that you can take to improve the performance of your site.
Another tool that you could use to check your page speed which would give you a more definite measurement is webpagetest.org. It was created by a chrome browser engineer at Google and it is an open source project that is free for use. What is good with this tool is that it loads your page in an actual browser from multiple locations and it gives you results for each specific page speed factor. All you would have to do is enter your url, set test location, browser to use, any advanced settings you prefer to set, then just start the test. The results would show you your time to first byte, start render, first contentful paint, speed index, web vitals, document complete, and fully loaded measurements. Based on SIA tests, the target is to get your TTFB to be below one second.
WebpageTest also has the option for more advanced testing that includes multi-step transactions, capture video, content blocking, compare first view verses repeat view, change the connection speed, etc. Additional information are also included through waterfall charts and resource loading reports. The best part is that, it is all free.
Another tool to check for your speed score is Pingdom. Same as with the other tools we’ve mentioned, it is also a free testing tool. It shows your site requests in a waterfall view and it allows you to filter data by load order, file size, and load times, etc. It also provides information on total requests, load time, and page size. It also gives you a speed performance rating similar to that of Google Page Speed Insight where you can get scored 0 – 100, each having different criteria and an individual score. Another benefit of using this tool is that it stores the results of all tests performed on your website, which allows you to track the improvements you have made.
Now that you know the importance of page speed and what exactly is Google referring to when they say page speed is a ranking factor, let us talk about different ways on how to increase your page speed metrics and improve your site’s time to first byte, both for mobile search and desktop search.
First step would be to do a site audit in order to have all the data on your site, particular metrics for each pages, content in the pages, any existing issues that can be fixed such as some 404 issues, redirect issues, etc. After you’ve fixed existing issues, you can check the speed score of your pages to see which particular pages are having speed issues that needs fixing.
Once you have determined which are which, here are some tips on what you can do to speed up those pages.
Images and graphics help with engagement and is also an important part of a webpage. However, images tend to be the largest files on a webpage and can slow down a site. To avoid this, optimize your images so that the image file size are not larger than they need to be, while still providing quality images. Check your image format. Image compression of your image files will help increase your load speed.
In addition, take away images that are unimportant and only keep relevant content on your page as the more images a page has, the slower it will load.
Optimizing your images can make a huge difference on your page speed.
Optimize your code by removing spaces, comma, and unnecessary characters. Remove code comments, formatting and unused code. Try to reduce the number of Javascript and CSS files, and try to group them together. Doing so will help reduce the number of http requests, and make for a faster loading time.
Redirects create additional http requests and multiple redirects negatively affect page speed, as it adds loading time to your pages. Aim to reduce redirects, if not needed.
Leverage your browser cache information so that when a visitor comes back to your site, the browser remembers it and does not have to reload everything all over again. This is mainly for repeat visitors accessing your page and does not apply to new users, but it still has its benefits.
Your server response time is affected by a lot of different factors such as the traffic, the resources each page uses, the software used by the server, and your hosting. Look for performance issues like slow database queries, slow routing, lack of memory, and fix time.
When it comes to hosting, you get what you pay for. There are three types of hosting – shared hosting, virtual private servers, also called VPS hosting, and dedicated servers. The most popular choice is shared hosting as it is the cheapest option. However, you share the server with multiple users which means slow page speeds.
Do not skimp on your hosting. Get a host that is reliable and that you can trust. Upgrade to a VPS host or better yet, go for a dedicated server. Moving to a quality host can give a huge impact and a faster site speed.
CDNs, also called content distribution network or content delivery network is a network of servers that are used to distribute the load of content based on location. Copies of your site are stored in multiple data centers so that users have faster and more reliable access to your site, wherever they may be. When you are hosting your site on a single server, all user requests are sent to the single hardware. Due to this, the time to process each request increases, especially if the user is far from the server and/or if there are multiple users sending a request. With a CDN, user requests are sent to the nearest server, which can deliver faster website speed.
Plugins are helpful components of a site and each has different features that can make the management of your site better. The downside of this is that, the more plugins you have on your site, the more resources are needed to run each of them. This causes a slow down in the loading of your site and sometimes, security issues can also come up.
Run a performance check on your site to be able to see which plugins may be slowing down your site. Avoid plugins that loads a lot of script and styles, or those that generate a lot of database queries. Go through your plugins and delete ones which you are not using anymore. Keep only the necessary ones and make sure that they are always up to date. Removing unnecessary plugins should be able to help make your site a fast site.
Now that you know what page speed Google is referring to when they say page speed is a ranking factor, and the negative impact of slow sites, we hope that with our tips, you would be able to get your site fixed and up to speed.
As we say, there are multiple ranking factors to getting a site ranked and page speed is just one of them. Make improvements in the different ranking signal that Google looks to when it comes to ranking sites in organic search and you will definitely be up in the top.
Not sure what the other factors are when it comes to search rankings? Check out our other articles or better yet, sign up for the SIA for tried and tested Search Engine Optimization information that would help you get that rank.